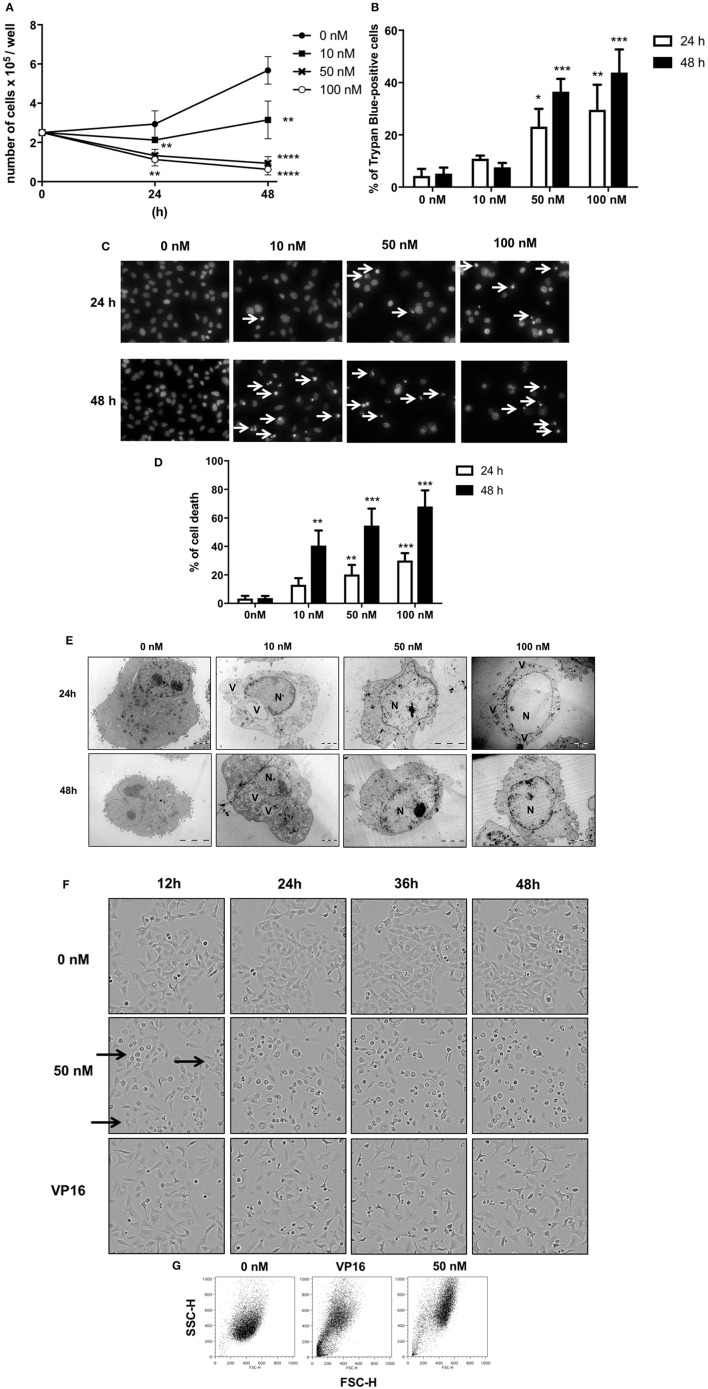
Figure 2.
Glucoevatromonoside exerts cytostatic and cytotoxic effects on A549 cells. (A) GEV reduces proliferation of A549 cells in a concentration-dependent manner; (B) analysis of cell death by trypan blue staining after 24 and 48 h of treatment at 10, 50, and 100 nM; (C) Hoechst staining; and (D) quantification of cell fractions presenting shrinking and fragmented nuclei (white arrows) in treated cells vs. untreated cells; (E) Representative transmission electron microscopy of A549 cells treated with 10, 50, and 100 nM of GEV after 24 and 48 h of treatment. Images show nuclear and cytoplasmic alterations. (N) nucleus and (V) vacuoles (F) Representative bright filter images obtained by IncuCyte™ videomicroscopy of cells treated with GEV (50 nM) and VP16 (50 μM) after 12, 24, 36, and 48 h (G) Flow cytometry analysis of forward-scattered light (FSC) vs. side-scattered light (SSC) of A549 cells treated with GEV (50 nM) and VP16 (50 μM) for 48 h. Arrows represent cells with increased cell volume and granularity. Statistical analysis: ANOVA-one way; Dunnett's post-hoc analysis in (C,E). Significance is reported as: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 compared to controls.