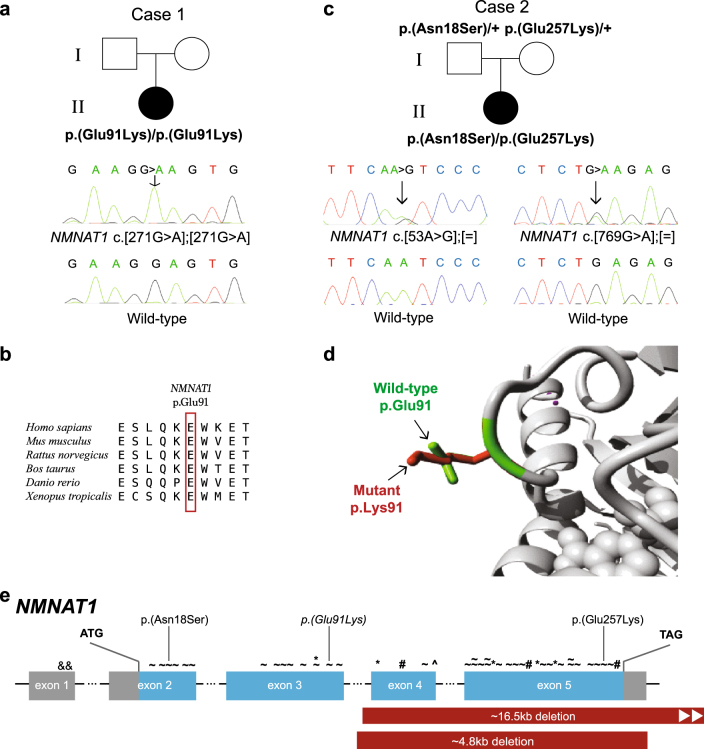
Fig. 2.
NMNAT1 variants and gene structure. a, c Pedigrees of Cases 1 and 2, respectively, showing affected proband, unaffected parents and respective genotypes where available and confirmatory Sanger traces. Wild-type Sanger traces are shown for comparison. b Amino acid sequence conservation across different species d Ribbon diagram showing region of NMNAT1 affected by the variant in Case 1. Differences in size and structure are shown between wild-type p.Glu91 (green) and mutant p.Lys91 (red). e NMNAT1 gene structure with previously reported variants marked above the affected exon as follows: & non-coding, ~ missense, * nonsense, # frameshift, ^ canonical splice site point variants. Partial gene deletions are indicated by solid red bars. The variants identified in this study are indicated above, with the homozygous variant italicised