Figure 4. Understanding Gut-Brain Cross-Talk: Therapeutic Targets for Treating Metabolic Disease.
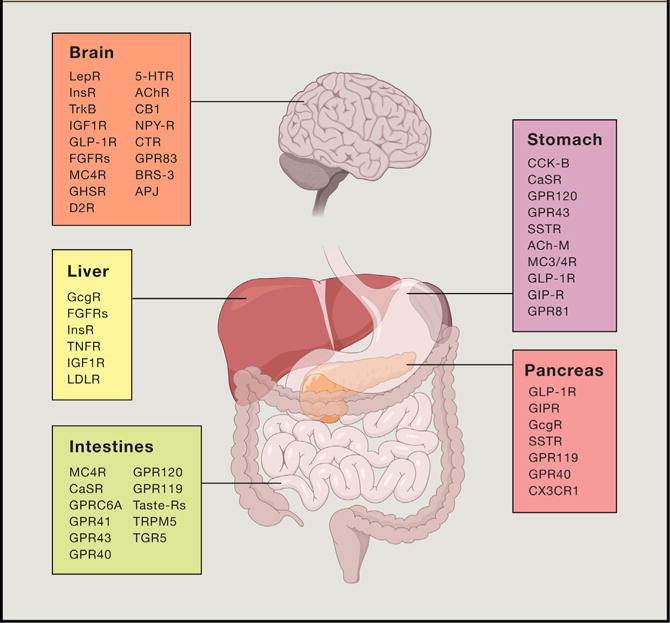
Current and promising therapeutic targets for treating obesity, type 2 diabetes, and associated co-morbidities are summarized. Future efforts hope to identify refined polypharmacy approaches intended to match the efficacy of the bariatric surgeries to cure obesity and diabetes. LepR, leptin receptor; InsR, insulin receptor; TrkB, tyrosine receptor kinase B; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; FGFRs, fibroblast growth factor receptors; MC4R, melanocortin receptor 4; GHSR, growth hormone secretagogue receptor; D2R, dopamine receptor D2; 5-HTR, serotonin receptors; AChR, acetylcholine receptors; CB1, cannabinoid receptor type 1; NPY-R, neuropeptide Y receptors; CTR, calcitonin receptor; BRS-3, Bombesin receptor subtype 3; AJP, Apelin receptor; GcGR, glucagon receptor; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptors; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; CaSR, calcium sensing receptor; GPR, G protein-coupled receptor; TRPM5, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 5; CCK-B, cholecystokinin B receptor; SSTR, somatostatin receptor; ACh-M, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; GIP-R, gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor; CX3CR1, fractalkine receptor.
