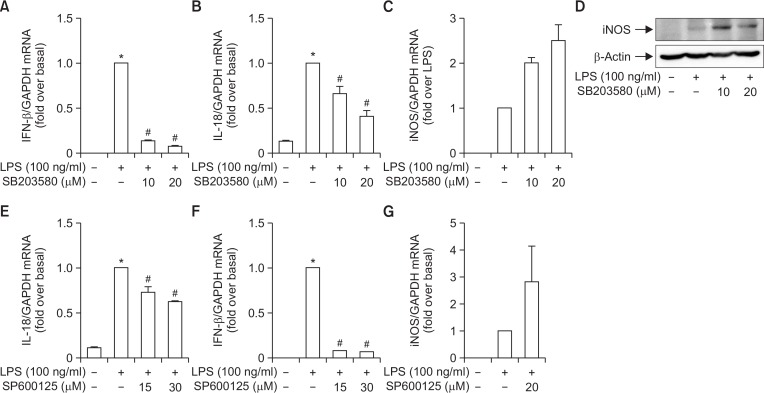
Fig. 6.
Role of p38MAPK and JNK signaling in the modulation of the expression of inflammatory mediators by YJI-7 in RAW 264.7 macrophages. (A, B) Cells were pretreated with SB203580, a pharmacological inhibitor of p38MAPK, followed by the incubation with LPS for 6 h. Expression levels of IFN-β (A) and IL-18 (B) mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR as described previously. Values represent the fold change in the mRNA expression level in relation to that detected in cells treated with LPS and are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=4). Statistical significance is indicated as follows: *p<0.05 for comparisons with values observed in control cells, #p<0.05 for comparisons with values observed in cells treated with LPS alone. (C, D) Cells were treated with LPS for 6 h in the absence or presence of SB203580. Messenger RNA (C) and protein expression (D) levels of iNOS were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses, respectively. (E–G) RAW 264.7 macrophages were pretreated with SP600125, a selective inhibitor of JNK, for 1 h followed by the stimulation with LPS for additional 6 h. IL-18 (E), IFN-β (F) and iNOS (G) mRNA expression levels were determined by qRT-PCR as indicated previously. Values represent fold change compared to LPS-stimulated cells and are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=4). *p<0.05 compared with control cells, #p<0.05 compared with cells treated with LPS alone.