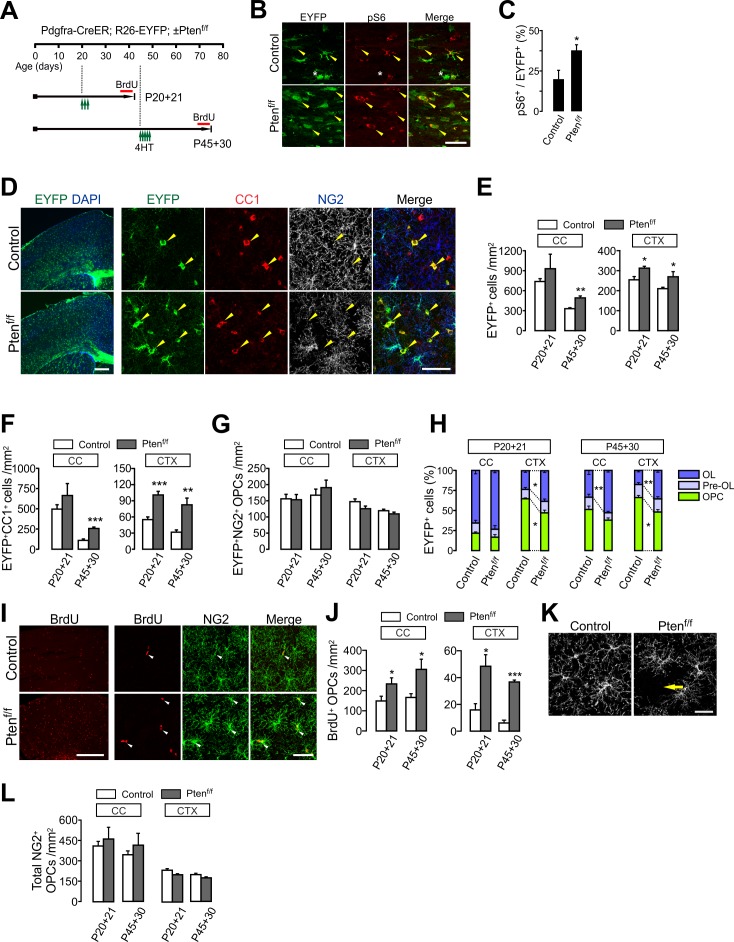
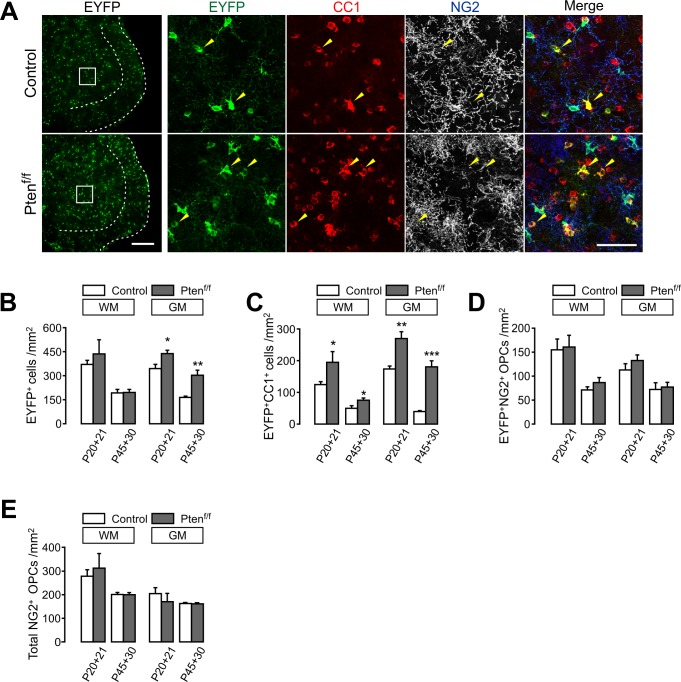
Figure 2. OPC-specific Pten ablation enhances oligodendrocyte differentiation and OPC proliferation in the brain.
(A) Experimental scheme for 4HT injection and BrdU administration into Pdgfra-CreER; R26-EYFP; ±Ptenf/f mice, and for mouse sampling. For P45 +30, 4HT (1 mg per injection) was injected five times between P45 and P47 (a total of 5 mg). (B) Confocal images of phosphorylated S6 ribosomal protein (pS6) and EYFP+ cells in the CC at P20 +21. Arrowheads and asterisks indicate EYFP+ pS6+ cells and EYFP+pS6- cells, respectively. Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Percentage of pS6+ cells among EYFP-labeled cells in the CC at P20 +21. n = 5 mice per group. (D) Fluorescence (left) and confocal (right) images of EYFP+ cells in the brains of the 4HT-administered control and Pten cKO mice (P20 +21). The confocal images were taken from the CTX. Arrowheads indicate EYFP+CC1+ mature OLs. Scale bars, 500 μm (left) and 50 μm (right). (E) Number of total EYFP+ cells was increased in the CTX of Pten cKO mice during the OPC fate analysis for the two age windows. (F) Number of EYFP+CC1+ OLs. (G) The numbers of EYFP+NG2+ OPCs were not changed by the Pten cKO. (H) Percentages of OPC, pre-OL and OL among EYFP-labeled cells. (I) Fluorescence (left) and confocal (right) images of BrdU+ cells in the CTX (P20 +21). Arrowheads indicate BrdU+NG2+ OPCs. Scale bars, 500 μm (left) or 50 μm (right). (J) Quantification of BrdU+NG2+ OPCs in the CC and CTX. (K) Confocal images showing disruption of tiled OPC distribution in the CTX of Pten cKO mice (P20 +21). An arrow indicates a cortical area devoid of an NG2+ OPC. Scale bar, 50 μm. (L) Number of total OPCs. Data are represented as mean ±S.E.M. n = 4 ~ 7 mice per group for P20 ~41. n = 3 ~ 5 mice per group for P45 ~P75. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. Unpaired Student's t-test. The numerical data for the graphs are available in Figure 2—source data 1.