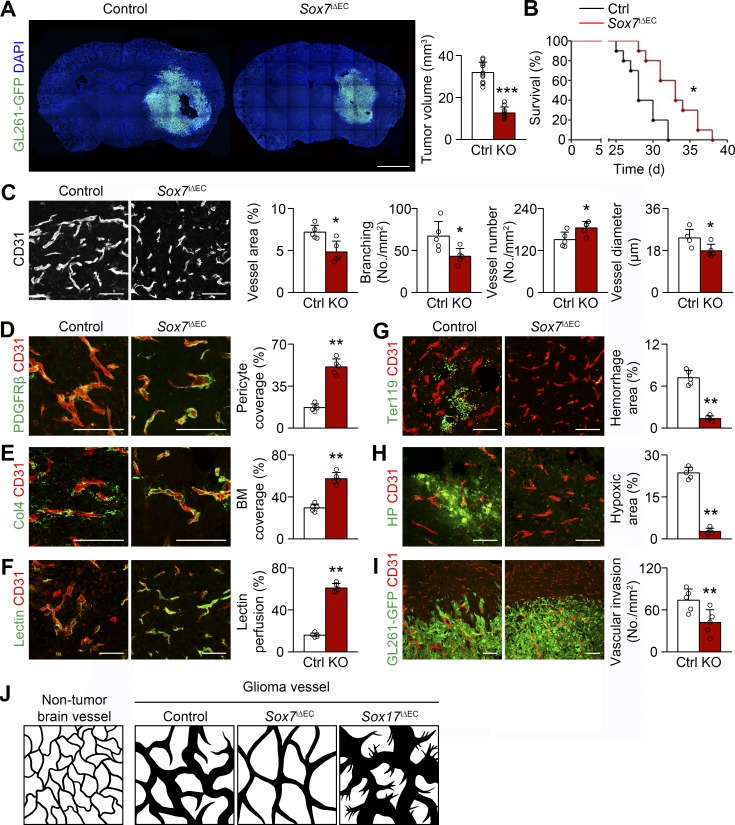
Figure 3.
Sox7 deletion delays HGG growth by reducing vessel abnormality. (A) GL261-GFP HGGs grown in control (Ctrl) and Sox7i△EC (KO) mice and quantification of tumor volume (n = 10). (B) Survival curves for HGG-bearing mice (n = 10). *, P < 0.05 (log-rank test). (C-I) CD31-positive HGG vessels in control and KO mice. (C) Normalized vessel morphology by Sox7 deletion and quantification of vessel area, branching, number, and diameter. (D and E) PDGFRβ-positive pericytes (D) and Col4-positive basement membrane (BM; E) and quantification of coverage. (F) Lectin and quantification of vascular perfusion. (G) Ter119-positive erythrocytes and quantification of hemorrhage. (H) Pimonidazole adduct (hypoxyprobe, HP) and quantification of hypoxic area. (I) Reduced perivascular invasion of GL261-GFP tumor cells by Sox7 deletion. (J) Diagrams depicting normal brain vessels and control, Sox7-deficient, and Sox17-deficient HGG vessels. Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5 unless otherwise denoted). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Bars: 2 mm (A); 100 µm (C–I).