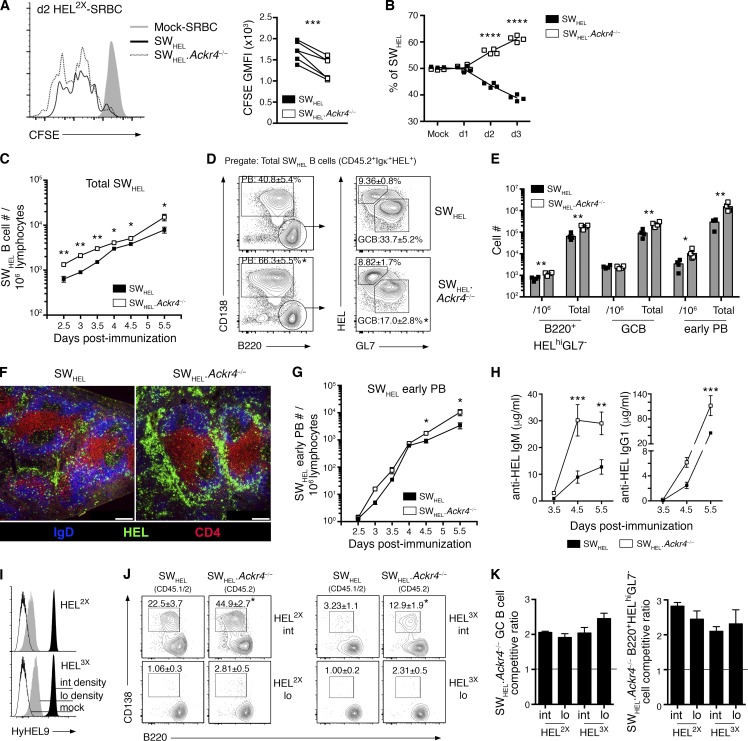
Figure 4.
ACKR4 limits early proliferation of antigen-engaged B cells and limits early PB responses. (A and B) WT (CD45.1/2) and Ackr4−/− (CD45.2) SWHEL B cells were cotransferred into B6.Ly5.1 (CD45.1) mice and immunized with HEL2X-SRBC. (A) Representative flow-cytometric CFSE profiles and analysis of CFSE GMFI among responding SWHEL B cells (B220+Igκ+HEL+CD138−) on day 2 (n = 6). Undivided SWHEL B cells were analyzed from mock-SRBC–immunized recipients (n = 2). (B) Contribution of WT and Ackr4−/− among responding SWHEL B cells (B220+Igκ+HEL+CD138−) over the first 3 d of the HEL2X-SRBC response (n = 4 mice/time point). (C–H) WT or Ackr4−/− (both CD45.2) SWHEL B cells were transferred into B6.Ly5.1 (CD45.1) mice and immunized with HEL2X-SRBC (n = 4 mice/genotype per time point). (C) Frequency of total responding SWHEL B cells (CD45.2+Igκ+HEL+) per 106 splenocytes (means ± SEM). (D) Representative plots of early PB and GC B cell and B220+HELhiGL7− cell responses as a frequency of total responding SWHEL B cells (plots are pregated CD45.2+Igκ+HEL+) on day 5.5. Numbers in plots represent the means ± SEM frequency of early PBs, GC B, or B220+HELhiGL7− cells as the frequency of the total responding SWHEL B cells. (E) Frequency of SWHEL B220+HELhiGL7− cells, GC B cells and early PBs (gated as shown in D) per 106 splenocytes and total number per spleen on day 5.5 (means ± SEM). (F) Representative histology of responding SWHEL B cells on day 5.5 (n = 4 mice/genotype). Bar, 200 µm. HEL, green; IgD, blue; and CD4, red. (G) Frequency of SWHEL early PBs (gated as in E) per 106 splenocytes (means ± SEM). (H) Anti-HEL IgM and IgG1 serum concentration as determined by ELISA (see Materials and methods; means ± SEM). (I–K) WT (CD45.1/2) and Ackr4−/− (CD45.2) were cotransferred into B6.Ly5.1 (CD45.1) recipients and immunized with HEL2X (intermediate affinity) or HEL3X (low affinity) conjugated to SRBCs at intermediate or low epitope densities (n = 4 mice/genotype per condition). (I) HEL2X or HEL3X were conjugated to SRBCs at intermediate (black histogram; 100 µg/ml; SRBC) and low (gray histogram; 5 µg/ml; SRBC) epitope densities and detected using HyHEL9 mAb. Mock-conjugated SRBCs (open histogram) are shown for comparison. (J) Representative plots of concurrent WT and Ackr4−/− SWHEL early PBs on day 5 (pregated Igκ+HEL+ and CD45.1+CD45.2+ [WT] or CD45.1−CD45.2+ [Ackr4−/−]). Numbers in plots represent the mean (± SEM) frequency of early PB as the frequency of total responding SWHEL B cells. (K) SWHEL.Ackr4−/− competitive ratio is plotted as the ratio of Ackr4−/− to WT among SWHEL GC B cell (left) or B220+HELhiGL7− cell (right) compartments (gated as in D), normalized to the input ratio, as determined from mock-SRBC–immunized mice. n = 4 mice (means ± SEM) on day 5. (A–K) *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; data are representative of two independent experiments. (A and J) Two-tailed, paired Student’s t test. (B and C–H) Two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. (C–K) Means ± SEM.