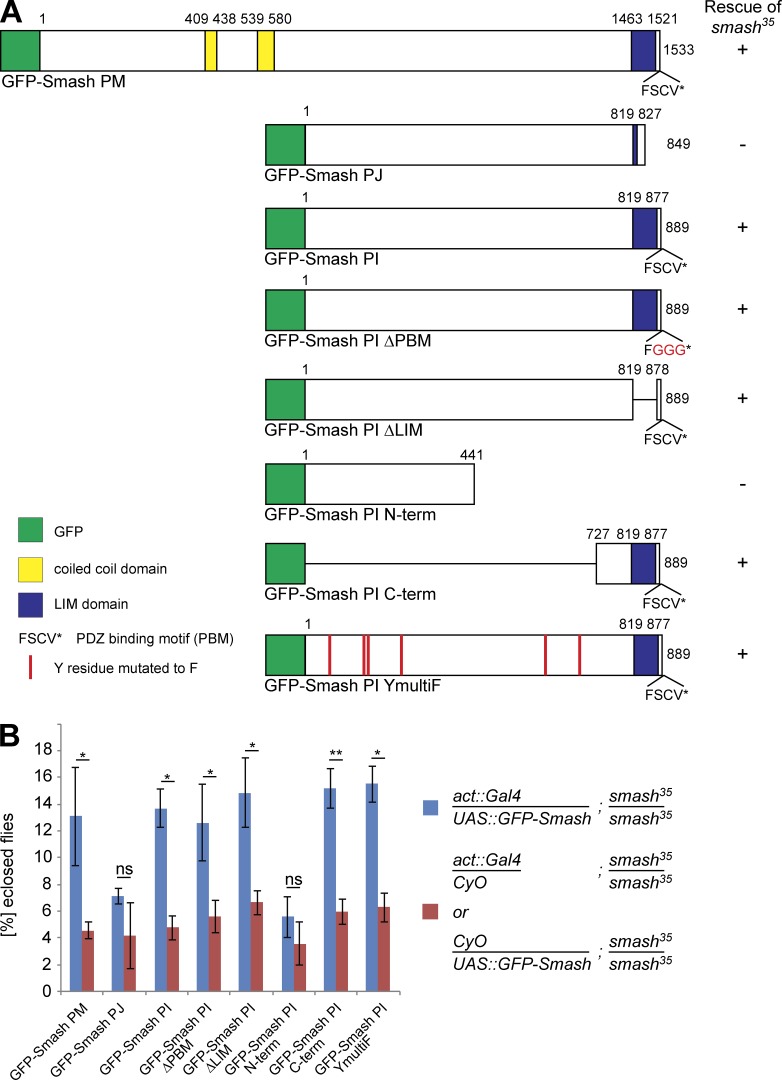
Figure 8.
Overexpression of GFP-Smash PM and GFP-Smash PI rescues semilethality of smash35 mutant animals. (A) GFP-Smash constructs used for the rescue assays. + or – in the column to the right indicates whether semilethality of smash35 is rescued. The number of eclosed smash35 homozygous adults expressing the respective GFP-Smash construct under control of the ubiquitous act5C::Gal4 driver line was compared with the number of eclosed smash35 homozygous mutant adults from the same cross carrying only act5C::Gal4 or the respective UAS::GFP-Smash construct as negative control. Rescue was scored (+) when the eclosion rate of smash35 homozygous mutant adults expressing the rescue construct was significantly (P < 0.05) higher than in the negative control. (B) Quantification of the rescue assays. Blue bars, mean percentage of animals with the respective genotype ± SEM; red bars, mean percentage of animals with the respective genotype divided by 2 ± SEM; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, not significant. GFP-Smash PM: P = 0.041, n = 663; GFP-Smash PJ: P = 0.143, n = 525; GFP-Smash PI: P = 0.014, n = 579; GFP-Smash PI ΔPBM: P = 0.045, n = 626; GFP-Smash PI ΔLIM: P = 0.033, n = 613; GFP-Smash PI N-term: P = 0.071, n = 875; GFP-Smash PI C-term: P = 0.009, n = 1072; GFP-Smash PI YmultiF: P = 0.021, n = 632.