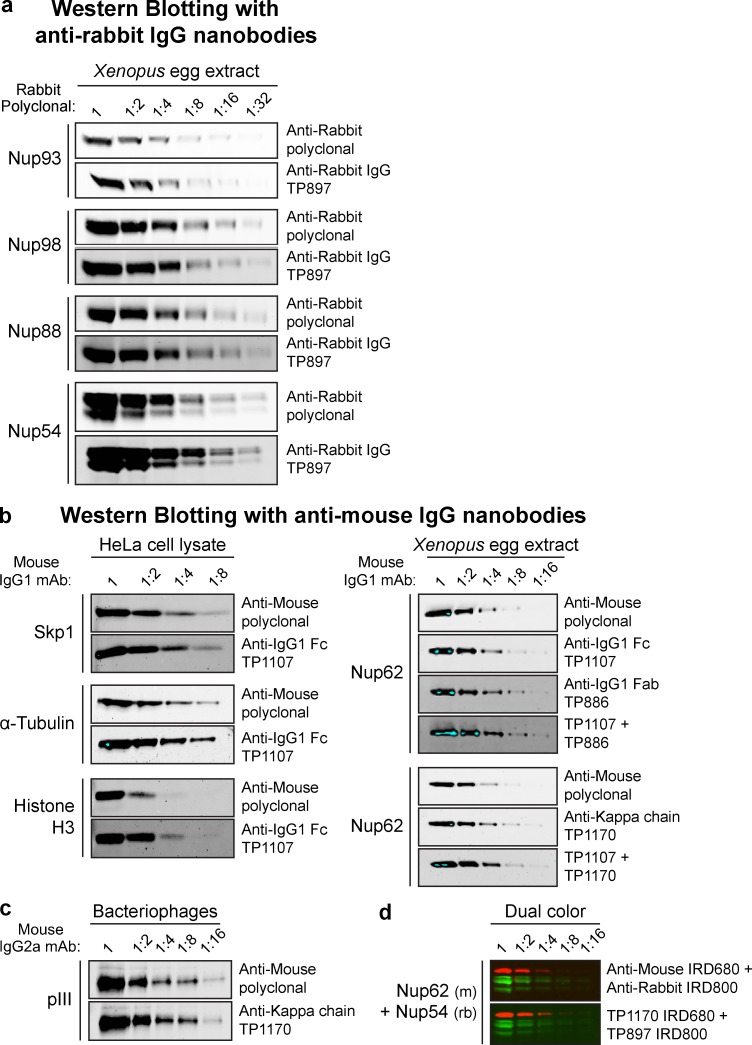
Figure 3.
Western blotting with infrared dye–labeled anti-IgG nanobodies. (a) A twofold dilution series of Xenopus egg extract was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. The indicated rabbit polyclonal antibodies were used to detect Nups. These primary antibodies were then decorated via either IRDye 800–labeled goat anti–rabbit polyclonal IgG (1:5,000; LI-COR Biosciences) or anti–rabbit IgG nanobody TP897 (10 nM). Blots were analyzed with an Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (LI-COR Biosciences). (b) Left: A twofold dilution series of HeLa cell lysate was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. The indicated mouse IgG1 mAbs were decorated via either IRDye 800–labeled goat anti–mouse polyclonal IgG (1:1,340, 5 nM; LI-COR Biosciences) or anti–mouse IgG1 Fc nanobody TP1107 (5 nM). Right: A twofold dilution series of Xenopus egg extract was blotted and probed with anti-Nup62 mouse IgG1 mAb A225. It was then detected via IRDye 800–labeled goat anti-mouse polyclonal IgG (5 nM), anti–mouse IgG1 Fc nanobody TP1107 (5 nM), anti–mouse IgG1 Fab nanobody TP886 (5 nM), anti–mouse κ chain nanobody TP1170 (2.5 nM), or a combination of TP1107 and TP886 or TP1107 and TP1170. Blue pixels indicate signal saturation. (c) A dilution series of filamentous bacteriophages was blotted and probed with an anti–minor coat protein pIII mouse IgG2a mAb. It was then decorated via either IRDye 800–labeled goat anti-mouse polyclonal IgG (2.5 nM) or anti–mouse κ chain nanobody TP1170 (2.5 nM). (d) Dual-color Western blotting. A twofold dilution series of Xenopus egg extract was blotted and probed with anti-Nup62 mouse IgG1 mAb A225 and rabbit anti-Nup54 polyclonal antibody. These primary antibodies were then detected via IRDye 800–labeled goat anti–rabbit polyclonal IgG and IRDye 680–labeled goat anti–mouse polyclonal IgG. Alternatively, they were detected with TP1107 coupled to IRDye 680 and TP897 coupled to IRDye 800.