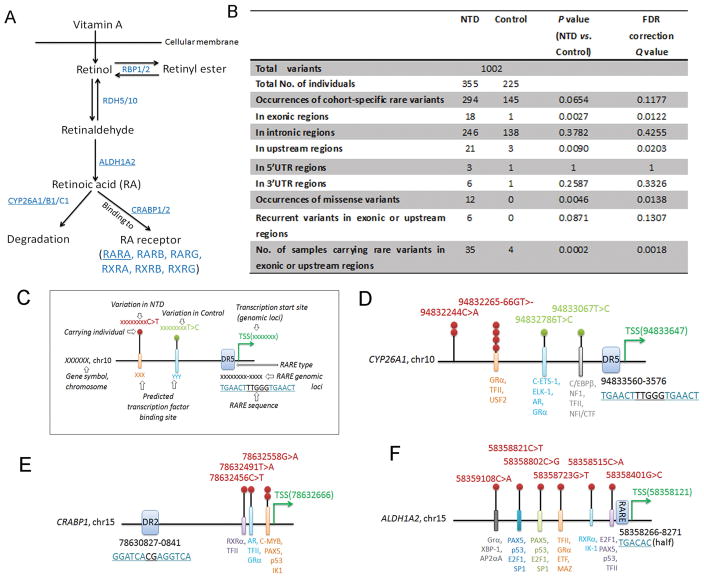
FIGURE 1. Retinoid related genes harbor rare variants in humans with neural tube defects.
A) A schematic of the synthesis and degradation of retinoic acid from vitamin A with the enzymes involved in retinoid metabolism and binding indicated in blue font. The genes sequenced in the present study are denoted by underlining of the encoded proteins. B) Rare variants were found in all sequenced genes in the present cohort of NTD cases relative to controls. P value was obtained via Fisher’s exact test and false discovery rate (FDR) correction. C) Illustration for each symbol in D-F. D-F) Schematics show the genomic positions of rare variants found in upstream regions of CYP26A1, CRABP1, and ALDH1A2 genes relative to the retinoic acid response-element (RARE) and predicted transcription factor binding sites.