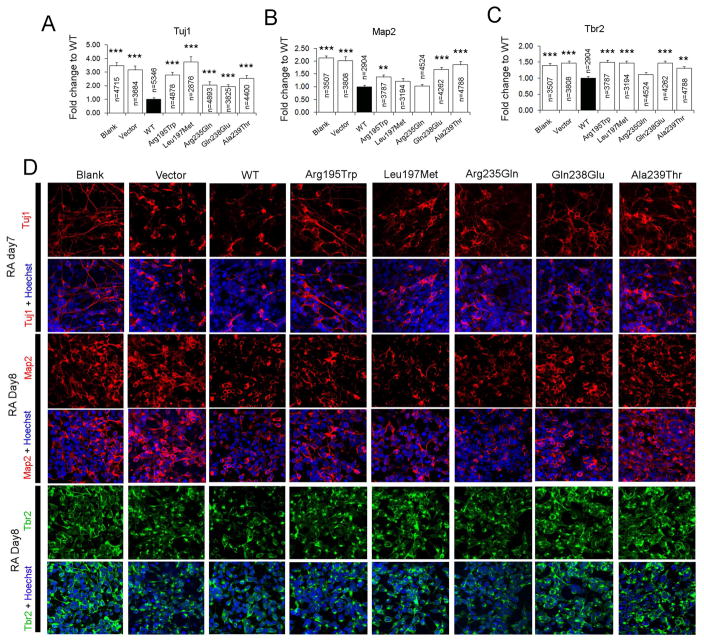
FIGURE 4. CYP26B1 variants disrupt modulation of neural differentiation.
Quantification of the immunofluorescent staining results of neuronal markers Tuj1 (A), Map2 (B) or Tbr2 (C) positive cells 7–8 days after RA treatment of NE-4C cells (Blank), or NE-4C cells transiently transfected with vector (Vector), wildtype CYP26B1 (WT), or different CYP26B1 variants. The percentage of immunopositive cells relative to all cells (Hoechst labeled) in a field of view were scored and then compared to cells transfected with WT CYP26B1. ***: P < 0.0001; **: P < 0.01; Student’s t-test. D) Typical images of the immunofluorescent staining used for calculations in A–C. For each genotype and neuronal marker, three to four replicates were performed.