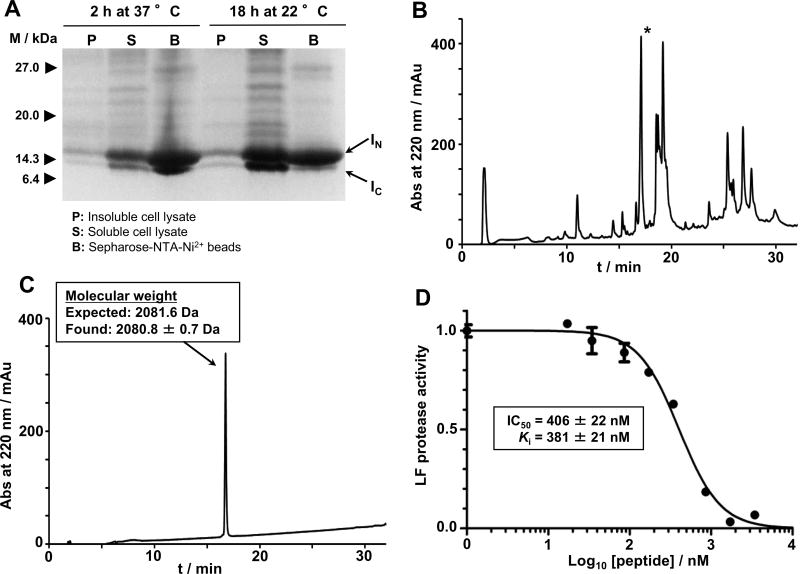
Figure 3.
In-cell expression of RTD-1 in E. coli cells using Npu DnaE intein-mediated PTS. A. SDS-PAGE analysis of the recombinant expression of RTD-1-intein precursor in Origami2(DE3) cells for in-cell production of RTD-1 at different induction conditions. B. Analytical HPLC trace of the solubilized cell lysate pellet obtained by inducing bacterial expression of the RTD-1 precursor for 18 h at 22 °C. The peak corresponding to the folded RTD-1 is indicated with an asterisk. C. Analytical HPLC and observed molecular weight by ES-MS of purified RTD-1. The calculated mass corresponds to the average isotopic mass. D. Biological activity of purified RTD-1. Inhibition assay of RTD-1 against anthrax LF protease. Different concentrations of RTD-1 were tested against LF protease. At each concentration, residual LF activity was measured and divided by the activity of LF in the absence of inhibitor. Activity was measured as the rate LF protease cleaves a fluorescence LF substrate43 and determined by the rate of fluorescence signal decaying (see the experimental section).