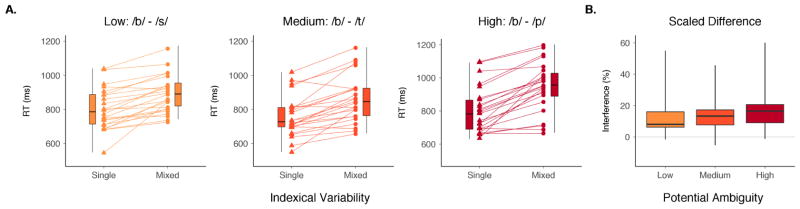
Figure 3. Effects of indexical variability and potential for acoustic-phonemic ambiguity across talkers on response times for consonant contrasts.
(A) Change in response times is shown for individual participants between the single- and mixed-talker conditions across three levels of potential inter-talker ambiguity. Boxplots in each panel show the distribution (median, interquartile range, extrema) for each variability-by-ambiguity condition. (B) The interference effect of indexical variability is shown for each level of potential ambiguity across talkers. The distribution of differences in response time between the mixed- and single-talker conditions is shown, scaled within-participant to their response time in the single-talker condition: ((mixed – single) / single) × 100. Significant interference was observed for every level of potential inter-talker ambiguity; the high-ambiguity condition showed a significantly greater interference effect than either the medium- or low-ambiguity conditions.