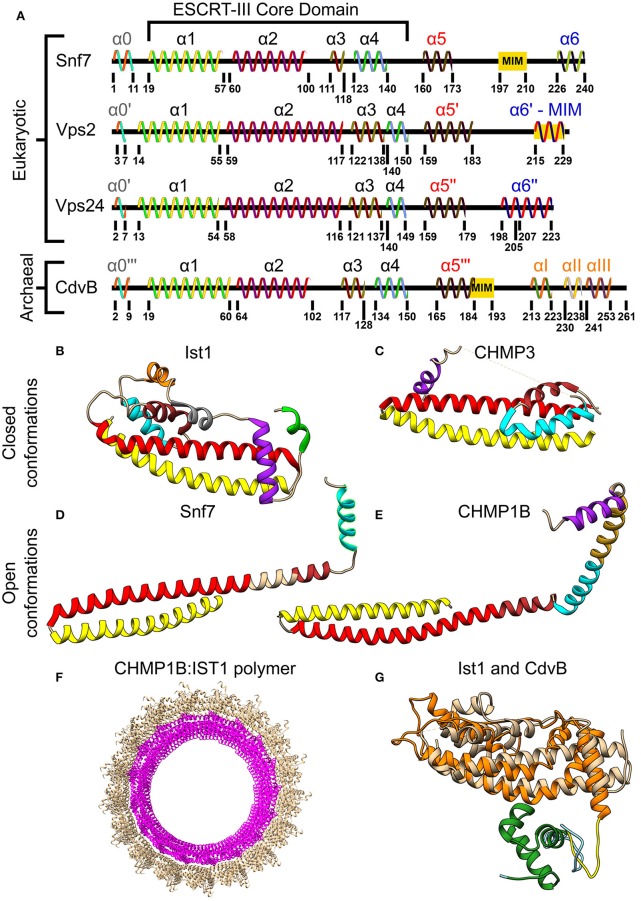
Figure 3.
Molecular structure of ESCRT-III and CdvB proteins. (A) Secondary structure of several S. cerevisiae ESCRT-III (Tang et al., 2015) and S. acidocaldarius CdvB proteins. ESCRT-III proteins—helices that are not part of the ESCRT-III core domain are shown with tags. For CdvB, the wH helices are numbered using Greek letters. Since no high-resolution structure of either Vps2 or CdvB exists, the numbering of the helices in these cases is only putative. (B,C) Closed conformation of the ESCRT-III proteins. (B) IST1 from Cryo-EM (PDB #3JC1) (McCullough et al., 2015). α1, Yellow; α2, Red; α3, Brown; α4, Cyan; α5, Purple; α6, Green. IST1 non-canonical helices are in orange and gray. (C) Crystal structure of CHMP3 (Residues 8–222, PDB # 3FRT) (Bajorek et al., 2009b). (D,E) Open conformation of ESCRT-III proteins. (D) S. cerevisiae Snf7 core domain (PDB #5FD9) (Tang et al., 2015). (E) CHMP1B from Cryo-EM (PDB #3JC1) (McCullough et al., 2015). Color code for (C–E) same as (B). Note that for CHMP1B the interfaces between α2 to α3 and α4 to α5 are only putative. (F) Cryo-EM structure of a reconstituted ESCRT-III positive curvature membrane binding ring (PDB ##3JC1). IST1 molecule in tan and CHMP1B in magenta. (G) Alignment of S. acidocaldarius CdvB Phyre2 based predicted structure and IST1 (PDB #3FRS, residues 1–189; Bajorek et al., 2009b). IST1 is shown in light tan. CdvB core domain is shown in orange, the wH domain in green and the MIT motif in yellow (the rest of the chain in cyan). RMSD distance between 131 atoms 4.916 Å.