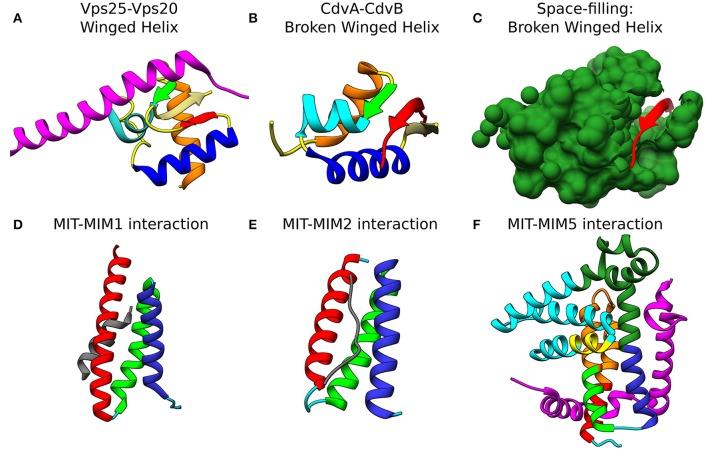
Figure 4.
Molecular basis for the interaction of ESCRT-III and CdvB proteins. Top row: wH interactions of ESCRT-III and CdvB proteins with upstream components. (A) Crystal structure of the Vps25-Vps20 interaction zone. Vps25 wH domain: αI, orange; β1, green; αII, cyan; αIII, Blue; β2, Khaki; β3, Red; unstructured regions, yellow. Vps20 interaction peptide in purple (PDB #3HTU) (Im et al., 2009). (B) S. solfataricus CdvA-CdvB “broken” wH interaction zone. Color representation—same as in (a) with the appropriate modification of the β-strands numbering (PDB #2XVC) (Samson et al., 2011). E3B peptide of CdvA in red. (C) Same as (B) with the CdvB wH (light sea green) in space filled representation. Bottom row: ESCRT-III and CdvB interact with downstream components through a MIM-MIT interactions. (D) Interaction between the Vps2 MIM1 (gray) and Vps4 MIT domain. (MIT helices; α1, red; α2, green; α3, medium blue; the rest of the chain in cyan). Based on PDB #2V6X (Obita et al., 2007). (E) Interaction of S. acidocaldarius CdvB MIM2 (gray) with CdvC MIT (PDB #2W2U). Helices colors, same as in (D) (Samson et al., 2008). (F) Interaction of Vps60 MIM5 (magenta) with Vta1 MIT (PDB #2LUH) (Yang et al., 2012). Helices colors, same as in (D). Homology regions between Vta1 and S. islandicus CdvC in orange and green. Homology between Vta1 and S. islandicus CdvB1 in yellow. The rest of the Vta1 chain is in cyan.