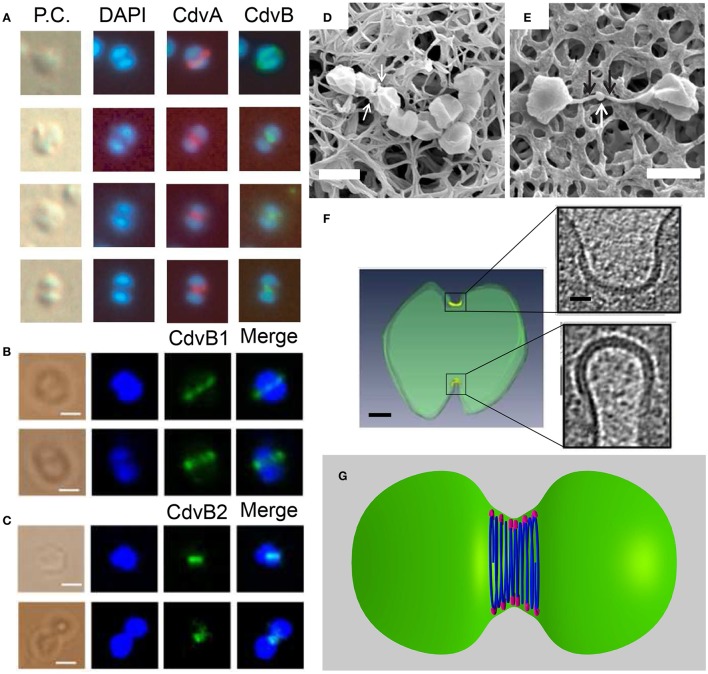
Figure 9.
The Cdv system in cytokinesis in Crenarchaeota. Left column: In situ immunofluorescence microscopy of Cdv proteins. (A) Intermediate steps during S. acidocaldarius cytokinesis showing localization of CdvA and CdvB bands that shrink in concomitant with the septum formation. P.C. denotes phase contrast. (B,C) Localization of S. islandicus CbvB1 (B) and CdvB2 (C) to the division site. The localization is visualized before chromosomes segregated (upper row in each panel) and during cytokinesis after chromosome segregation (lower raw in each panel). Scale bars 1 μm. (D) Mutant S. islandicus cells expressing a reduced level of CdvB1 are locked in a “chain-like” phenotype and cannot separate. (E) Mutant S. islandicus cells over-expressing CdvB2 form a “mid-body” like phenotype. Scale bars for (D,E) 2 μm. (F) Cryo-EM segmented image of a dividing S. acidocaldarius cell. Cell membrane is denoted in green and the thick protein belt at the cleavage furrow is denoted in yellow. Insets - zoom in of the two sides of the cleavage furrow. Scale bars - 150 nm for the whole cell, 40 nm for the insets. (G) “Hourglass” model of the Cdv system during cytokinesis in dividing S. acidocaldarius cell, showing CdvB polymers (blue) that are connected to the membrane via CdvA (purple). For clarity, CdvA is shown only at the top and bottom of the cell. In reality, it is located along the whole perimeter of the cell. (A) Is reproduced from Lindås et al. (2008) with permission, Copyright (2088) National Academy of Sciences. (B–E) Are reproduced from Liu et al. (2017) with permission. (F) Is reproduced from Dobro et al. (2013) with permission.