Figure 6.
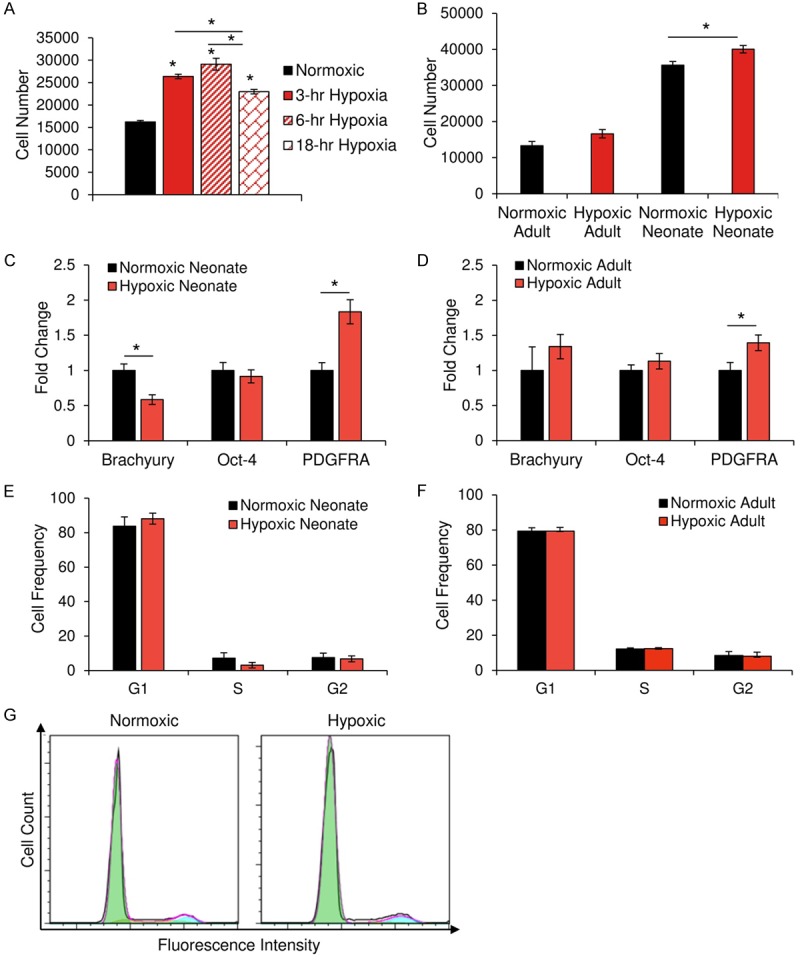
CPCs experience improvements in invasive ability without a change in developmental status. Invasiveness in response to SDF-1α, a chemoattractant, was assessed using the Transwell® invasion assay. In response to SDF-1α, CPCs invade through matrigel into a reservoir, where they are then stained with calcein AM and measured by spectrophotometry in quadruplicate. (A) Quantification of the invasiveness of a representative CPC clone following exposure to hypoxia for various lengths of time. A significant increase in cell invasion was noted for each time point, with six hours of hypoxia inducing the greatest level of invasive activity. While both neonatal and adult CPCs that are pretreated with hypoxia exhibit improved invasiveness (B; n=10), only neonatal CPCs experienced significant improvements. RT-PCR was used to examine the effects of short-term hypoxia on the expression of differentiation markers present in neonatal (C; n=4) and adult (D; n=3) CPCs. Flow cytometry of propidium iodine-stained CPCs revealed no significant change in the cell cycle profile of neonatal (E; n=6) or adult (F; n=9) CPCs following treatment with hypoxia. A representative histogram (G) of flow cytometry-based cell cycle analysis. *P < 0.05. Values reported as the average ± S.E.M.
