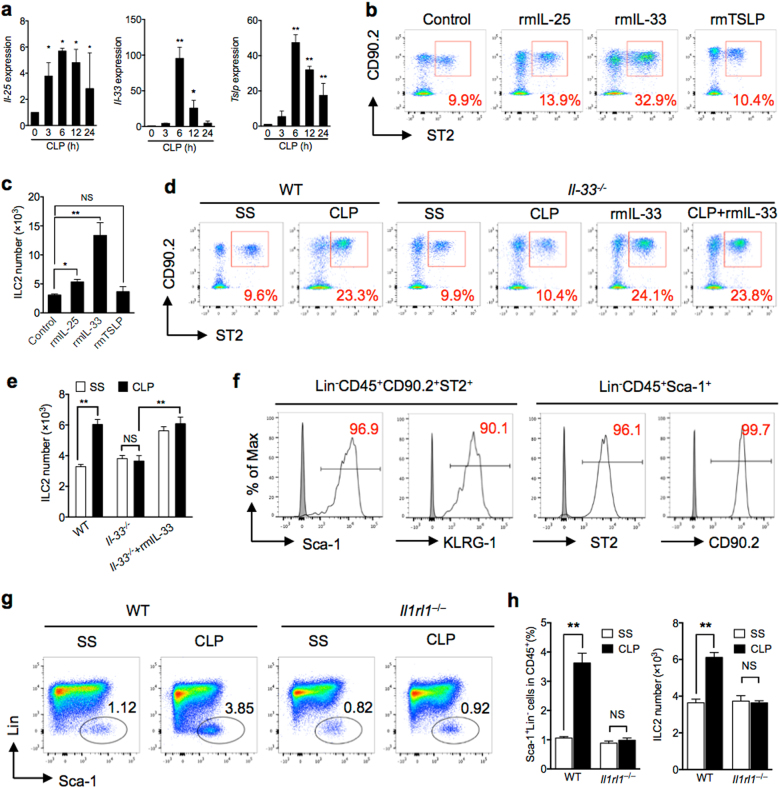
Fig. 2. IL-33/ST2 signaling is required for sepsis-induced ILC2 recruitment.
a RT-qPCR expression of Il-25, Il-33, and Tslp mRNA in lung tissue, which are relative to 18 s, at time points up to 24 h after CLP compared to SS of each time points (n = 3–5 mice/group). b Representative FACS plots and c bar graph showing absolute number of ILC2 in lungs harvested from control (PBS), rmIL-25, rmIL-33, and rmTSLP-treated mice (1 μg in 50 μl PBS intratracheal (n = 5 mice/group). d Representative flow cytometry plots and e absolute number of lung ILC2 (Lin−CD45+CD90.2+ST2+) in WT and Il-33−/− mice with/without rmIL-33 treatment mice at 24 h after CLP or SS. Data are representative of three experiments, n = 3–6. f Expression of ILC2-identifying cell surface markers (Sca-1 and KLRG1) on Lin−CD45+CD90.2+ST2+ cells, and expression of ST2 and CD90.2 on Lin−CD45+Sca-1+ cells. g Bar graphs showing representative FACS plots and h absolute cell number of lung ILC2 in WT or Il1rl1−/− mice as above (n = 5 mice/group). The plots were gated at CD45+ cells. Data shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, NS not significant