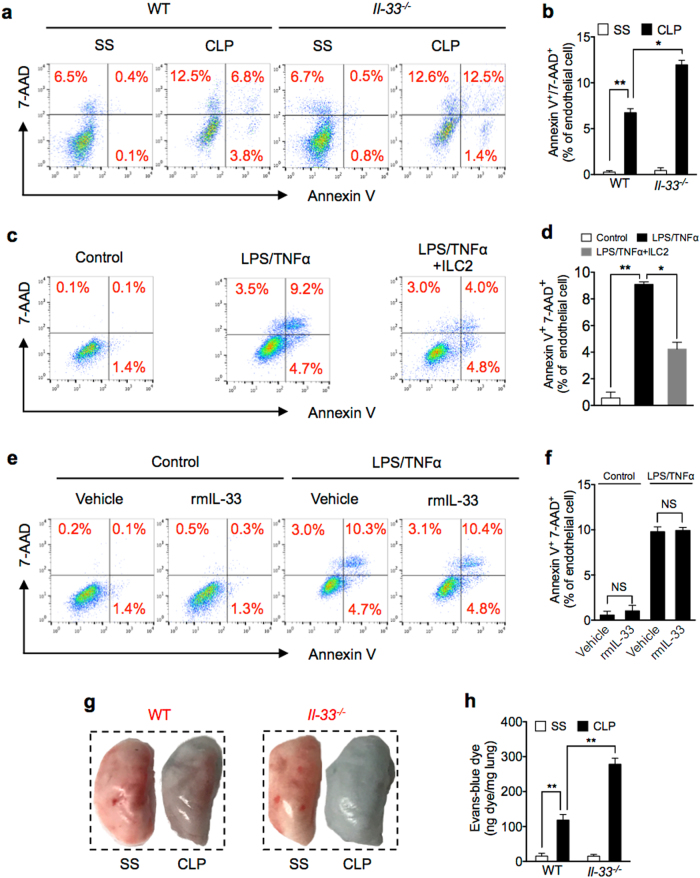
Fig. 3. ILC2 protect lung EC from death following sepsis.
a Representative flow cytometry plots of Annexin V/7-AAD staining of MLEC from WT and Il-33−/− mice at 24 h after SS or CLP. MLECs were identified as CD31+ and Annexin V/7-AAD double-stained cells were analyzed as dying (n = 5 mice/group). b Bar graph of Annexin V/7-AAD double-stained cells as a percentage of MLEC in WT and Il-33−/− mice at 24 h after SS or CLP. c Representative flow cytometry plots of Annexin V/7-AAD staining of in vitro primary isolated MLEC from WT mice cultured alone (control), with LPS (1 μg/ml) + TNFα (20 ng/ml), or LPS + TNFα + co-culture with ILC2 (1 × 104 cells/well) for 24 h. d Bar graph of Annexin V/7-AAD double-stained cells as a percentage of total MLEC. e Representative flow cytometry plots and f bar graph of Annexin V/7-AAD staining of purified MLEC from WT mice cultured with LPS (1 μg/ml) + TNFα (20 ng/ml) and with or without rmIL-33 (50 ng/ml) for 24 h. g Representative images of whole lungs stained with Evans blue dye from WT and Il-33−/− mice at 24 h following SS or CLP. h Colorimetric quantitative analysis of Evans blue dye extracted from stained lungs from WT and Il-33−/− mice at 24 h following SS or CLP (n = 5 mice/group). Data are representative of three independent in vitro experiments. Data shown are the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01