Figure 2.
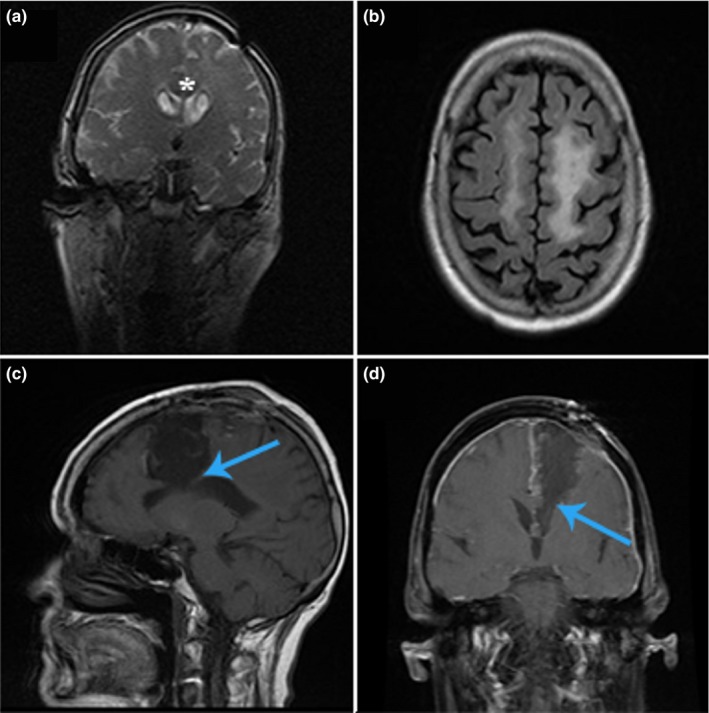
Permanent supplementary motor area (SMA) syndrome, case 1. Patient with a low‐grade glioma of the left frontoparietal region, hyperintensities seen on coronal T2 (a) and on sagittal T2 FLAIR (b) imaging. Postresection of tumor revealing dissection through the SMA into the corpus callosum (CC) on T1 with (d) and without (c) contrast (blue arrows). Asterisks in (a) designate location of CC
