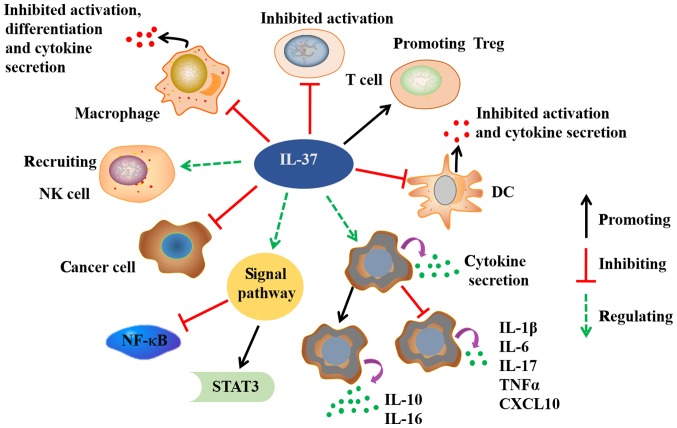
Figure 2.
Possible biological functions of IL-37. IL-37 exerts significant anti-inflammatory, anticancer, immune deviatory, immunosuppressive, and metaboregulatory effects. IL-37 dramatically reduces the cytokines secretion in macrophages and DCs. The activation and differentiation of macrophages, DCs and T cells are also inhibited by IL-37. In addition to healthy tissues, IL-37 is variably expressed in many cancer cells. IL-37 exerts antitumor immune responses through recruiting NK cells into tumors tissues. The binding of IL-37 to its receptor activates STAT-3, and inhibits NF-kB signals. IL, interleukin; STAT-3, signal tranducer and activator of transcription 3; NF-kB, nuclear factor kB; DC, dendritic cell; Treg, T regulatory cell; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine 10.