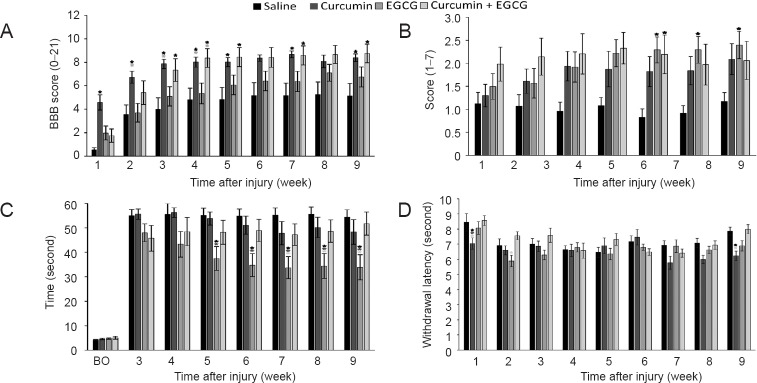
Figure 1.
Locomotor and sensory recovery in rats following curcumin and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) application after spinal cord injury.
(A–C) The effect of curcumin, EGCG, and their combination on locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury was evaluated using the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) open-field locomotor test (A), flat beam test (B), and flat beam time score (C). Animals treated with combined therapy of curcumin and EGCG, or curcumin alone, performed significantly better in the BBB open-field locomotor test than animals treated with saline. In the flat beam test, EGCG treated animals showed the best recovery, followed by curcumin + EGCG treated animals. (D) The thermal nociception was evaluated using the plantar test. No additional hyperalgesia was found after application of any of the used drugs. Two-way repeated measures analysis of variance with the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. *P < 0.05 (The color of asterisks indicates the statistically different group(s)).