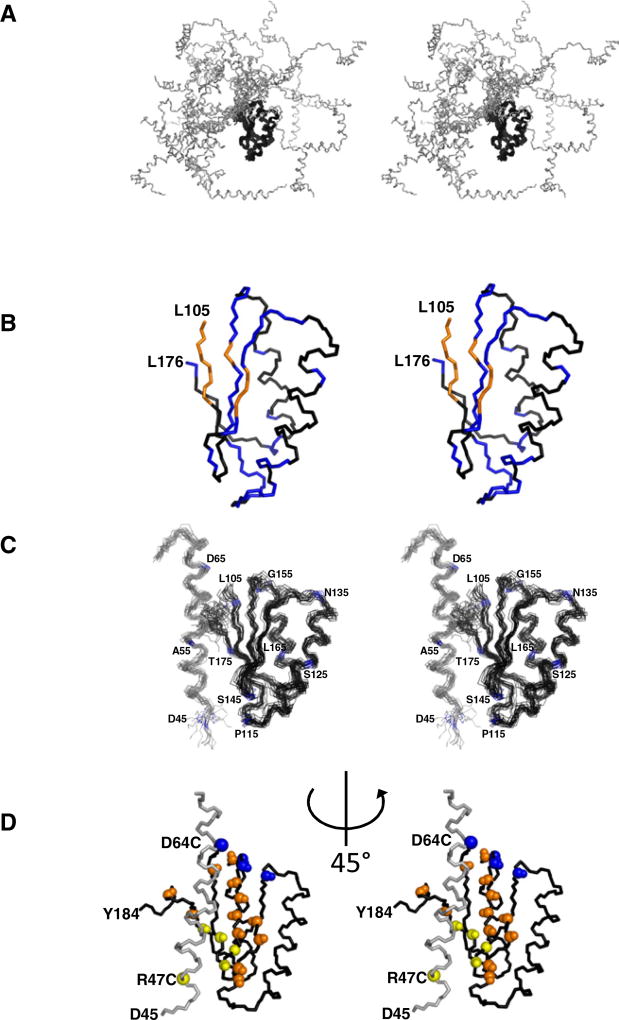
Figure 2. The Model for the Structure of the Conserved Core Region of MESD Corresponding to Residues 45–184.
(A) The “open form” backbone view of the 20 energetically lowest conformers of MESD45–184 achieved by a structure calculation using the CYANA protocol (Guentert, 2004) for the assignment of ambiguous NOE distance restraints. Only the “core domain” (residues 104–177, black) converges to a globular structure.
(B) NMR solution structure of MESD89–184. The amide signals of all colored residues are shifted in the 1H-15N-HSQC-NMR spectrum of MESD45–184. Δδ1H > 0.02 ppm or Δδ15N > 0.2 ppm. The amide signals of blue-marked residues are back shifted to the core domain chemical shifts in the 45–184 fragment carrying the W61R mutation. W61R mutant amide resonances of the orange-colored residues are not in superposition with any of the wild-type truncation.
(C) The “closed form” model structure of MESD45–184 based on the chemical shift perturbations shown in (B). The model has been enforced by 656 possible assignments of NOE distance restraints, 226 dihedral angle restraints empirically obtained from Talos (Cornilescu et al., 1999), and 36 RDCs. Residues 71–103 of the flexible loop region are omitted.
(D) Relaxation enhancement by introducing paramagnetic labels. Backbone amide groups affected (>50% reduction of peak height) by attachment of the paramagnetic MTSL label to C47 or C64 are colored in yellow and blue, respectively. Orange-colored backbone NH groups are affected from both spin labels. All views are in stereo. N and C termini (D45 and Y184) are marked. Orientation of (D) is rotated anticlockwise by 45° with respect to (A)–(C). See also Figure S1.