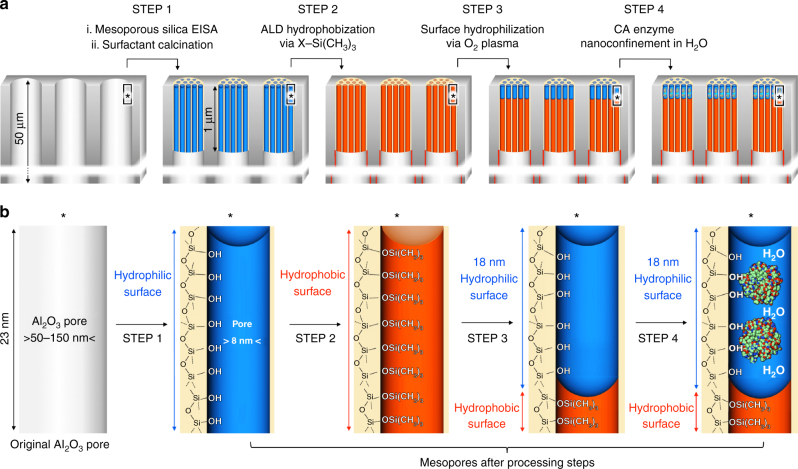
Fig. 4.
Design steps of the enzymatic liquid membrane. Beginning with a 50-µm-thick Anodisc support, Step 1 comprises the formation of oriented arrays of 8 nm diameter cylindrical silica mesopores within the 50–150 nm diameter Anodisc pores via evaporation-induced self-assembly followed by calcination to remove the P123 surfactant. In Step 2, three alternating cycles of atomic layer deposition (ALD) of HMDS ((CH3)3-Si-N-Si(CH3)3) + TMCS (Cl-Si(CH3)3) followed by water are conducted to convert the hydrophilic silanol-terminated mesopore surfaces to hydrophobic Si-O-Si(CH3)3 surfaces throughout the 1 µm length of the mesopore. In Step 3 a remote oxygen plasma treatment is used to regenerate hydrophilic silanol groups to a depth of 18 nm on the top surface. In Step 4 an aqueous solution of CA is introduced on the top surface. Through capillary condensation, water plus enzymes fill the mesoporous silica array. a images represent the processing steps and b images represent the corresponding surface chemistries