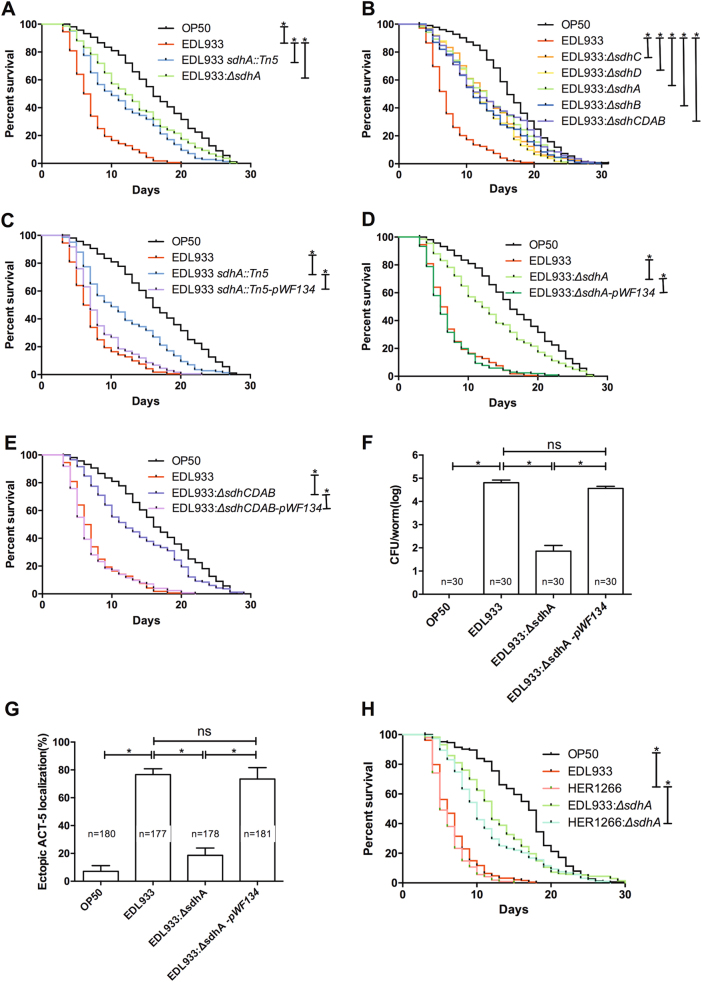
Fig. 2. Effect of the sdhA mutation on the pathogenicity of EHEC in C. elegans.
a The survival of N2 worms fed with E. coli strain OP50, wild-type EHEC strain EDL933, the isogenic transposon-generated mutant strain EDL933 sdhA::Tn5, and the isogenic sdhA deletion mutant strain EDL933:ΔsdhA were examined. The EDL933 sdhA::Tn5 strain (median N2 lifespan = 10.5 ± 1.5 days, P < 0.0001) and the EDL933:ΔsdhA strain (median N2 lifespan = 12.0 ± 2.0 days, P < 0.0001) were both significantly less toxic than the wild-type EDL933 strain (median N2 lifespan = 6.5 ± 0.5 days). b The survival of N2 worms fed with OP50, wild-type EDL933, and EDL933 with deletion of sdhC, sdhA, sdhD, sdhB, or sdhCDAB operon were examined. Deletion of sdhC (EDL933:ΔsdhC) (median N2 lifespan = 13.0 ± 2.0 days, P < 0.0001), sdhD (EDL933:ΔsdhD) (median N2 lifespan = 11.5 ± 1.5 days, P < 0.0001), sdhB (EDL933:ΔsdhB) (median N2 lifespan = 12.0 ± 1.0 days, P < 0.0001) genes, and the entire sdhCDAB operon (EDL933:ΔsdhCDAB) (median N2 lifespan = 12.5 ± 2.5 days, P < 0.0001) were all significantly less toxic than the wild-type EHEC strain EDL933 (EDL933) (median N2 lifespan = 6.75 ± 0.25 days). c–e The survival of N2 worms fed with sdhA transposon-generated mutant EDL933 sdhA::Tn5, sdhA deletion mutant (EDL933:ΔsdhA), sdhCDAB deletion mutant (EDL933:ΔsdhCDAB), and isogeneic strains rescued by the transformation of the sdhCDAB operon expression plasmid pWF134 (EDL933 sdhA::Tn5-pWF134, EDL933:ΔsdhA-pWF134, EDL933:ΔsdhCDAB-pWF134, respectively) were examined. c The decreased pathogenic phenotype in the EDL933 sdhA::Tn5 (median N2 lifespan = 10.5 ± 1.5 days) was restored by the sdhA gene complementation EDL933 sdhA::Tn5-pWF134 (median N2 lifespan = 7.0 ± 0.1 days, P < 0.0001). d EDL933:ΔsdhA (median N2 lifespan = 12.00 ± 2.00 days) and EDL933:ΔsdhA-pWF134 (median N2 lifespan = 6.0 ± 1.0 days, P < 0.0001). e EDL933:ΔsdhCDAB (median N2 lifespan = 12.5 ± 2.5 days) and EDL933:ΔsdhCDAB-pWF134 (median N2 lifespan = 5.5 ± 0.5 days, P < 0.0001). The median lifespan of N2 worms fed with wild-type EDL933 was 6.5 ± 0.5 days. f The number of bacteria colonized in C. elegans was determined by the colony-forming units (CFUs) assay from three independent experiments. The average CFU per infected worm fed with the sdhA deletion mutant was significantly decreased (7.10 × 101, P < 0.0001) compared to that of the wild-type EDL933 infected animals (6.43 × 104). The average CFU per infected worm fed with the sdhA gene complementation strain (3.65 × 104, P = 0.1) was similar to that of the wild-type EDL933 infected animals. The asterisk denotes statistically significant (P < 0.0001) examined by the t-test, and error bars indicate the SEM (standard error of mean) of three independent experiments. The total numbers of infected animals examined in each group are indicated by n. g Quantification of the ectopic mCherry::ACT-5 signal in GK454 nematodes exposed to OP50, EDL933, sdhA deletion mutant (EDL933:ΔsdhA), or sdhA gene complementation strain (EDL933:ΔsdhA-pWF134) at 20 °C for 4 days. The asterisk denotes statistically significant (P < 0.0001) examined by the t-test, and error bars indicate the SEM of three independent experiments. The total numbers of infected animals examined in each group are indicated by n. h Survival of N2 worms fed with the E. coli O157:H7 strain HER1266 and the isogenic strain with sdhA deletion. Deletion of sdhA in HER1266 (HER1266:ΔsdhA) confers the attenuated toxic phenotype (median lifespan of N2 animals = 10.0 ± 0.1 days, P < 0.0001). The median lifespan of N2 worms fed with wild-type HER1266 was 5.50 ± 0.5 days