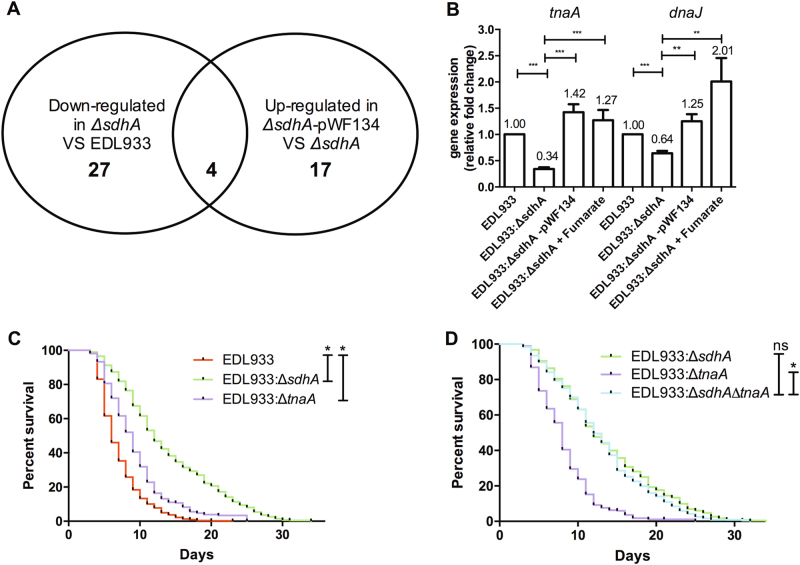
Fig. 6. TnaA is a downstream virulence effector of sdhA identified by proteomic analysis.
a The diagram shows that four differentially expressed proteins, which downregulated in the sdhA mutant (EDL933:ΔsdhA) and upregulated in the sdhA complement strain (EDL933:ΔsdhA-pWF134), were identified by our proteomic analysis. b The mRNA levels of tnaA and dnaJ in EHEC wild-type strain (EDL933), EDL933:ΔsdhA mutant strain (EDL933:ΔsdhA) the sdhA gene complementation strain (EDL933:ΔsdhA-pWF134) and 2.5 mM fumarate-treated sdhA (EDL933:ΔsdhA + Fumarate) were examined. Relative transcriptional expression was normalized to the expression of rpoA. The asterisk denotes statistically significant (P < 0.0001) examined by the t-test, and error bars indicate the SEM of three independent experiments. c The survival of N2 worms fed with the wild-type strain (EDL933) and the isogenic deletion strains of tnaA (EDL933:ΔtnaA) and sdhA (EDL933:ΔsdhA) were examined. Deletions of tnaA (median N2 lifespan = 8.0 ± 0.1 days, P < 0.0001) and sdhA (median N2 lifespan = 12.4 ± 1.8 days, P < 0.0001) all conferred the attenuated toxic phenotype compared to the wild-type EDL933 (median N2 lifespan = 6.4 ± 0.9 days). d The survival of N2 worms fed with the wild-type strain (EDL933) and the isogenic deletion strains of tnaA (EDL933:ΔtnaA), sdhA (EDL933:ΔsdhA), and the sdhA and tnaA double mutant (EDL933:ΔsdhAΔtnaA) were examined. The virulence of sdhA and tnaA double mutant (EDL933:ΔsdhAΔtnaA, median N2 lifespan = 13.5 ± 0.7 days) was similar to the EDL933:ΔsdhA (median N2 lifespan = 13.5 ± 2.1 days, P = 0.474). The asterisk denotes statistically significant (P < 0.0001) examined by the log-rank test, and “ns” represents no significant difference statistically