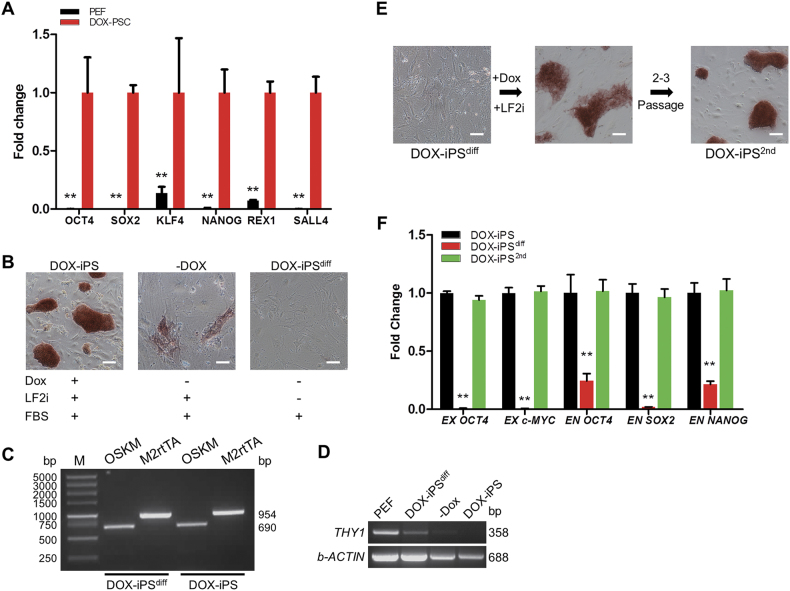
Fig. 1. Characterization of doxycycline-inducible porcine iPS cells.
The DOX-iPSCs were cultured in LF2i medium with or without doxycycline. a Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of pluripotent genes in DOX-iPSCs and PEF cells. b Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining of DOX-iPSCs and the differentiated DOX-iPS (DOX-iPSdiff) cells. c PCR analysis of transgenes from TetO-FUW-OSKM and FUW-M2rtTA in DOX-iPSCs and DOX-iPSdiff cells. d RT-PCR analysis of THY 1 expression in PEF, DOX-iPSdiff cells, and DOX-iPSCs. –Dox, cells were cultured without the addition of Dox. b-ACTIN was as internal control. e DOX-iPSdiff cells were reprogrammed in the medium with LF2i and Dox for 2–3 passages. The cells derived from DOX-iPSdiff cells were named DOX-iPS 2nd cells and were stained for AP. f Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of transgenes (EX) and endogenous pluripotent genes (EN) in DOX-iPSCs, DOX-iPSdiff, and DOX-iPS2nd cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. Data indicate mean ± SD; ** P < 0.01, n = 3