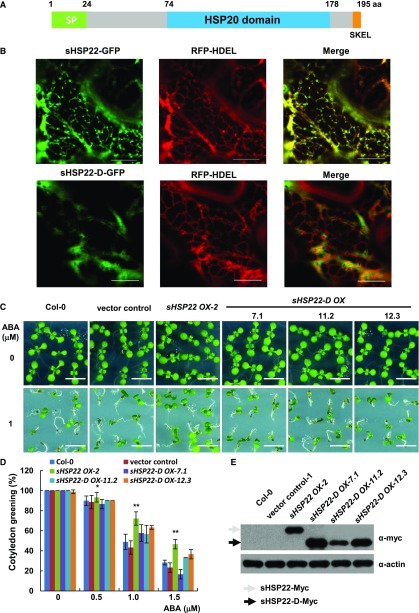
Figure 5.
ER localization of sHSP22 contributes to ABA response. A, Schematic diagram of the sHSP22 structure. Representative parts of signal peptide, HSP domain, and ER retention tetrapeptide are shown in green, light-blue, and orange boxes, respectively. B, Colocalization of sHSP22-GFP (top) and sHSP22-d-GFP (bottom) with RFP-HDEL. RFP-HDEL is an ER localization peptide motif fused with RFP. Tobacco leaves were infiltrated with agrobacteria bearing 35S:sHSP22-GFP and 35S:RFP-HDEL or 35S:sHSP22-d-GFP and 35S:RFP-HDEL constructs. After 3 d, tobacco leaves were cut and simultaneously subjected to confocal microscopy observation. C, Cotyledon greening phenotype of Col-0, vector control, sHSP22 OX-2, and sHSP22-D overexpression plants. Representative seedlings were sown 9 d after imbibition on 1 μm ABA. Bar = 0.5 cm. D, Statistical analysis of different genotype plants shown in C. The cotyledon greening percentage was calculated after the 9-d growth in the medium. The error bars represent ±sd (triplicate measurements; n = 90). The asterisks indicate a significant difference between sHSP22 overexpression and control plants (**P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05). E, sHSP22-D accumulation in overexpressing and control plants by western blotting using anti-myc antibody. The gray and black arrows separately denote whole and truncated sHSP22 protein form respectively. Actin is used as control.