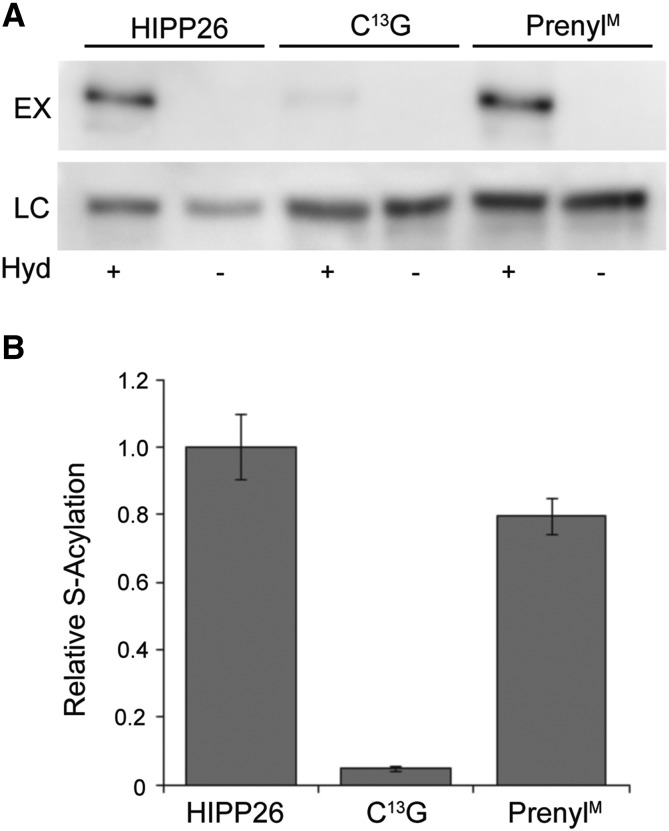
Figure 4.
HIPP26 S-acylation. A, HIPP26 was S-acylated under normal plant growth conditions at Cys-13. S-Acylation was determined by the Acyl-RAC assay. Free Cys residues were blocked with N-ethylmaleimide. S-Acyl groups on Cys residues within proteins were cleaved by hydroxylamine (Hyd +) to reveal free sulfhydryls. Sulfhydryl-reactive thiopropyl Sepharose beads were used to capture free sulfhydryl-containing proteins. Negative controls lacked hydroxylamine (Hyd −). Signal strength in experimental lanes (EX Hyd+) showed the level of S-acylation. Loading controls (LC) demonstrated equal loading of hydroxylamine-treated and -untreated samples onto thiopropyl Sepharose beads. B, Relative quantification of blots shown in A. Mutation of the C-terminal CVVM motif Cys (PrenylM) had a small effect on the S-acylation state (n = 2; P = 0.103 by one-tailed Student’s t test), while changing Cys-13 to Gly effectively abolished S-acylation (n = 2; P = 0.05). Values were calculated as intensity in EX Hyd+ lanes divided by intensity in LC Hyd+ lanes. Values are means represented as the proportion of wild-type HIPP26 S-acylation. Error bars indicate sd.