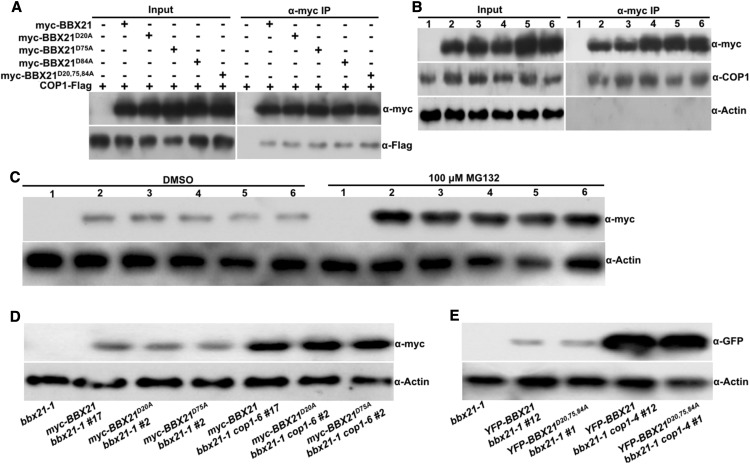
Figure 3.
COP1 promotes the degradation of BBX21 with impaired B-box domains in darkness. A, Co-IP analysis showing that myc-BBX21D20A, myc-BBX21D75A, myc-BBX21D84A, or myc-BBX21D20,75, 84A interacts with COP1. Total protein was extracted from Arabidopsis protoplasts expressing 35S:COP1-Flag, 35S:myc-BBX21, 35S:myc-BBX21D20A, 35S:myc-BBX21D75A, 35S:myc-BBX21D84A, and 35S:myc-BBX21D20,75,84A. The immunoprecipitates were detected using anti-Flag and anti-myc antibodies. B, Co-IP analysis showing that myc-BBX21D20A, myc-BBX21D75A, myc-BBX21D84A, or myc-BBX21D20,75,84A interacts with COP1 in Arabidopsis seedlings. Four-day-old white-light-grown bbx21-1 (1), myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 #17 (2), myc-BBX21D20A bbx21-1 #2 (3), myc-BBX21D75A bbx21-1 #2 (4), myc-BBX21D84A bbx21-1 #6 (5), and myc- BBX21D20,75, 84A bbx21-1 #3 (6) seedlings were transferred to darkness for 16 h and then subjected to a co-IP assay using anti-myc antibodies, with the immunoprecipitates detected using anti-COP1 and anti-myc antibodies. Actin served as a negative control. C, Immunoblot analysis of myc-tagged wild-type or various mutated BBX21 protein levels in dark-grown bbx21-1 (1), myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 #17 (2), myc-BBX21D20A bbx21-1 #2 (3), myc-BBX21D75A bbx21-1 #2 (4), myc-BBX21D84A bbx21-1 #6 (5), and myc- BBX21D20,75, 84A bbx21-1 #3 (6) transgenic seedlings treated with DMSO or 100 μm MG132 for 3 h. E, Immunoblot analysis of myc-BBX21, myc-BBX21D20A, and myc-BBX21D75A protein levels in myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 #17, myc-BBX21D20A bbx21-1 #2, myc-BBX21D75A bbx21-1 #2, myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 cop1-6 #17, myc-BBX21D20A bbx21-1 cop1-6 #2, and myc-BBX21D75A bbx21-1 cop1-6 #2 transgenic seedlings grown in the dark for 4 d. F, Immunoblot analysis of YFP -BBX21 and YFP -BBX21D20,75,84A protein levels in YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 #12, YFP-BBX21D20,75,84A bbx21-1 #2, YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 cop1-4 #12, and YFP-BBX21D20,75,84A bbx21-1 cop1-4 #2 transgenic seedlings grown in the dark for 4 d. In D to F, bbx21-1 served as a negative control, and anti-actin served as a loading control.