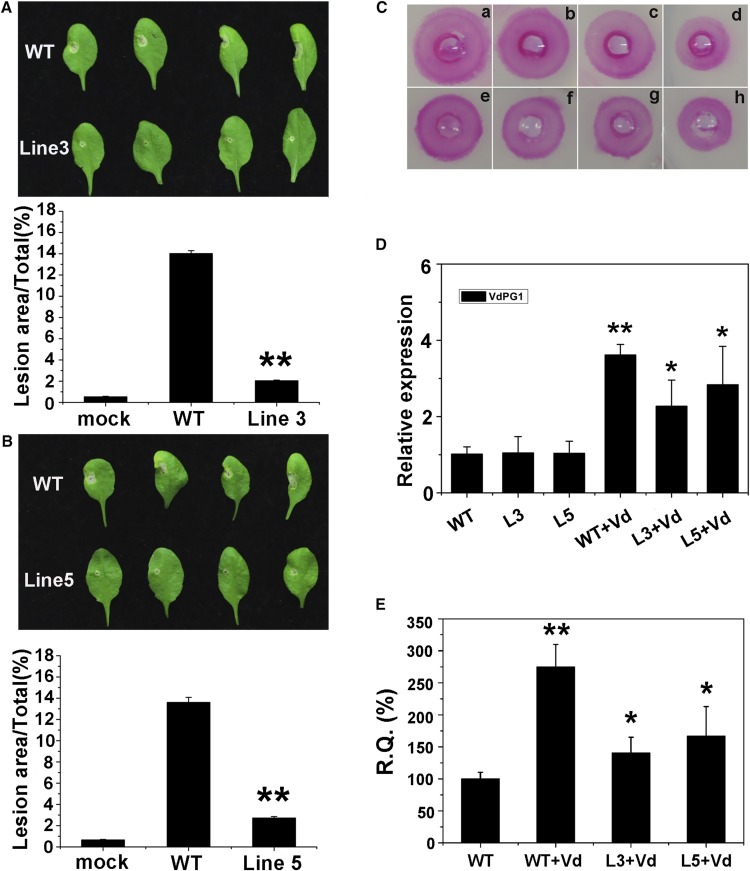
Figure 8.
Reduction of disease symptoms following V. dahliae infiltration, and detection of GhPMEI3 activity in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. A and B, Disease symptoms (top) and disease lesion size (bottom) of wild-type and transgenic Arabidopsis plants after inoculated with V. dahliae at 5 d postinoculation. The inoculum (10 μL) was placed on each leaf: the right half of the leaf was inoculated with 10 μL of Czapek liquid medium; the left half of the leaf was inoculated with 10 μL of V. dahliae. The lesion size was quantified using ImageJ software. The experiment was repeated three times (n = 20) with similar results. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from the wild type (Student’s t test, **P < 0.01). C, Inhibitory activity of GhPMEI3 in transgenic plants. a, 1 mU of purified GhPME2; b to d, GhPME2 with 15 μg of crude GhPMEI3 preparation from wild-type, or transgenic line 5 and 3 plants; e, 1 mU of purified GhPME31; f to h, GhPME31 with 15 μg of crude GhPMEI3 preparation from wild-type, or transgenic line 5 and 3 plants. D, Relative VdPG1 levels in wild-type and transgenic plants. The data are presented as the means ± se (n = 20). The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from the wild type (Student’s t test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). E, RT-qPCR quantification of fungal biomass in 100 mg of transgenic Arabidopsis tissues compared to untransformed wild type. All experiments were performed three times, each time in triplicate (n = 20). Data from a representative experiment were analyzed using Student’s t test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.