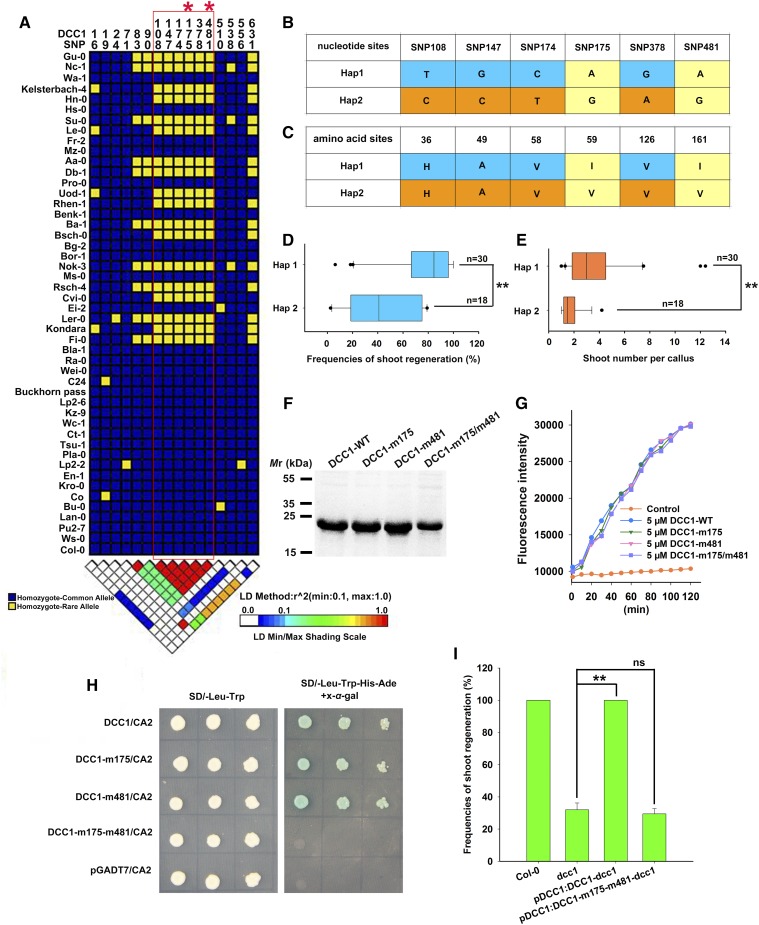
Figure 11.
DCC1 regulates the capacity of shoot regeneration among different Arabidopsis ecotypes. A, Linkage disequilibrium analyses of DCC1 in 48 Arabidopsis ecotypes indicated six critical SNPs (SNP 108, 147, 174, 175, 378, and 481). B, Two haplotypes (Hap1 and Hap2) of DCC1 were characterized based on six SNPs of nucleotide sequences in Arabidopsis natural variants. C, Amino acid sequences of Hap1 and Hap2. Two SNPs (SNP 175 and 481) resulted in amino acid mutations (I59V and I161V). D and E, Shoot regeneration frequencies from calli (D) and number of shoots per callus (E) in each haplotype group (n, number of genotypes belonging to each haplotype group). F, Purified proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. DCC1-WT from Col-0 was used as the control. DCC1-m175, DCC1-m481, and DCC1-m175/m481 were mutated according to Hap2 SNPs (SNP 175 and 481). G, Insulin reduction assay by the various proteins. Purified proteins were subjected to a reduction assay by using FiTC-insulin as the substrate, which displayed higher fluorescence after disulfide reduction. The assay mixture lacking recombinant proteins served as the control. Fluorescence intensity was recorded at 515- to 525-nm emission after 480- to 495-nm excitation for 120 min in a fluorescent plate reader at room temperature. H, Both SNP 175 and SNP 481 were critical for the interaction of DCC1 and CA2 by yeast two-hybrid assay. I, Frequencies of shoot regeneration from calli of wild-type Col-0, dcc1, pDCC1:DCC1-dcc1, and pDCC1:DCC1-m175-m481-dcc1 on SIM at 28 d. Significant differences are indicated: **, P < 0.01 and ns, P > 0.05 (Student’s one-tailed t test).