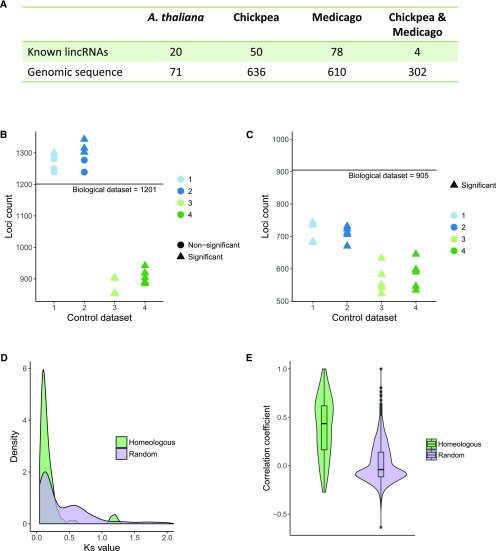
Figure 3.
Conservation of lincRNA loci in chickpea, M. truncatula, and Arabidopsis. A, Number of soybean lincRNA loci showing sequence similarity with lincRNAs or genomes of other species. B, Number of soybean lincRNA loci in biological and control datasets showing positional similarity with lincRNAs in other species. C, Number of soybean lincRNA loci in biological and control datasets showing positional similarity with other lincRNAs in soybean genome. D, Ks values calculated for protein-coding gene pairs flanking homeologous lincRNA loci and a random selection of homeologous protein-coding gene pairs (n = 444). The distribution of Ks values representing random selection has two peaks corresponding two duplication events. The protein pairs flanking homeologous loci mostly represent single, more recent duplication. E, Correlation of expression between homeologous lincRNA and a random selection of lincRNA pairs (n = 3,000). Homeologous loci have higher levels of coexpression.