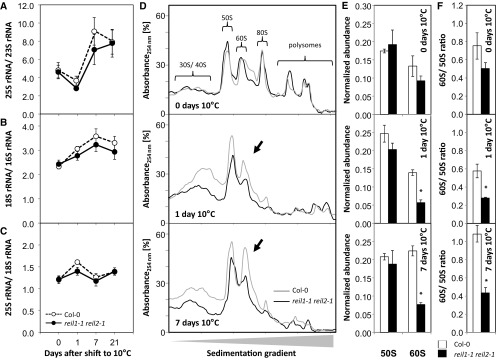
Figure 5.
Relative abundance of rRNAs within total RNA preparations and of 60S and 50S large ribosomal subunits from total ribosome preparations before and after the shift to 10°C. Complete reil1-1 reil2-1 rosettes were compared with wild-type (Col-0) rosettes in the nonacclimated state (i.e. at 0 d) and at 1, 7, and 21 d after transfer to the cold according to cultivation scheme C in Figure 1. A, Ratio of the cytosolic 25S large subunit rRNA relative to chloroplast 23S rRNA (P = 0.001). B, Ratio of the cytosolic small subunit 18S rRNA relative to chloroplast 16S rRNA (P = 0.003). C, Ratio of the cytosolic 25S large subunit rRNA and cytosolic 18S small subunit rRNA. For A to C, data are means ± se (n = 3–4 preparations from independent pools of mature rosette leaves). D, Representative sedimentation profiles of total ribosome preparations from ∼100 mg fresh weight of rosettes sampled at days 0, 1, and 7 of acclimation to 10°C. The sedimentation analysis was optimized for the separation of the 50S to 60S fractions. Indicated fractions were monitored by blank gradient subtracted absorbance (A254). Fraction identity was verified by rRNA analysis (Supplemental Fig. S3). E, Analysis of ribosome sedimentation profiles shown in D by calculating the normalized A254 abundance of the 60S and 50S fractions relative to the sum of all observed fractions (means ± se of n = 3 preparations from independent pools of mature rosette leaves). F, Ratio of the 60S fraction relative to the 50S fraction calculated from the data sets of E and F (means ± se of n = 3 preparations from independent pools of mature rosette leaves). The experimental design was according to scheme C in Figure 1. Mutant and wild-type plants were shifted at developmental stage ∼1.10. Nonacclimated rosettes were cultivated at 20°C and assayed immediately before the temperature shift. Peak areas of rRNA were determined from total RNA extracts by microfluidic electrophoresis. 23S rRNA was determined by the sum of two naturally occurring postmaturation cleavage products. For A to C, significance (P) of the time effect was tested by two-way ANOVA. For E and F, asterisks indicate significant changes of the mutant compared with the wild type (P < 0.05, heteroscedastic Student’s t test).