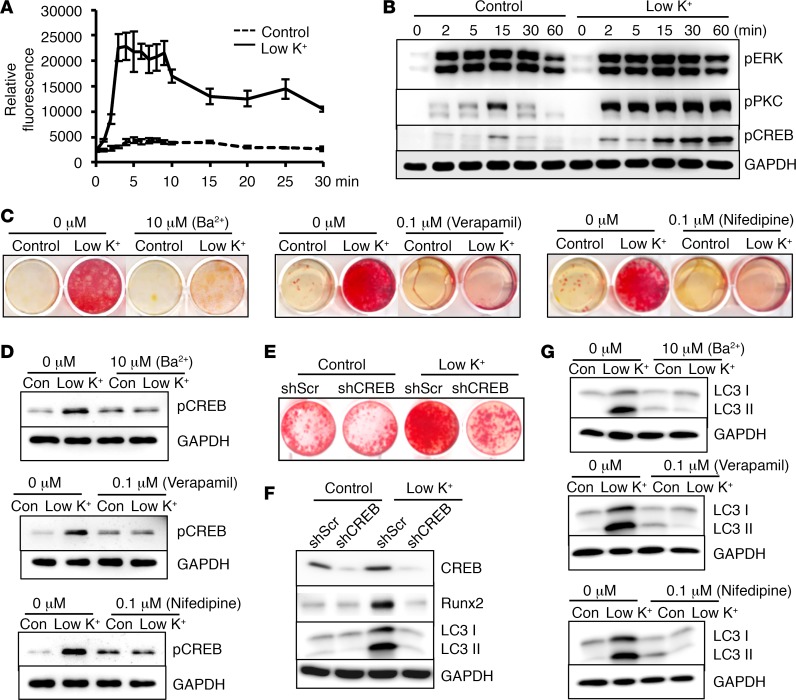
Figure 4. Activation of calcium signaling–mediated CREB was required for low-potassium-induced VSMC calcification.
(A) Effects of potassium levels on intracellular calcium, determined by Fluo4 NW, in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) exposed to control (5.4 mM) or low potassium (3.7 mM, Low K+). Results from 3 independent experiments are shown. (B) Effects of low potassium on activation of extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK), protein kinase C (PKC), and calcium-activated cAMP response element–binding protein (CREB), determined by Western blot analysis. Representative blots from 3 independent experiments are shown. (C) Effects of pharmacological inhibitors on VSMC calcification. VSMCs were exposed to control or low-potassium media with the indicated inhibitors for 3 weeks. Calcification was determined by Alizarin red staining. (D) Effects of pharmacological inhibitors on activation of CREB. Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of CREB in C. Representative images from 3 independent experiments are shown. (E and F) Effects of CREB knockdown on low-potassium-induced VSMC calcification. VSMCs with CREB knockdown by shRNA (shCREB) or control shRNA (shScr) were exposed to control or low-potassium media for 3 weeks. Calcification was determined by Alizarin red staining. Western blot analysis was performed to determine the expression of CREB, runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), and the autophagic marker, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), in the cytoplasmic form (LC3 I), and conjugated form (LC3 II). Representative blots from 3 independent experiments are shown. (G) Effects of pharmacological inhibitors on autophagy markers. Western blot analysis of LC3 I and II levels in VSMCs exposed to control or low-potassium media for 3 weeks, in the presence or absence of indicated inhibitors. Representative results from 3 independent experiments are shown.