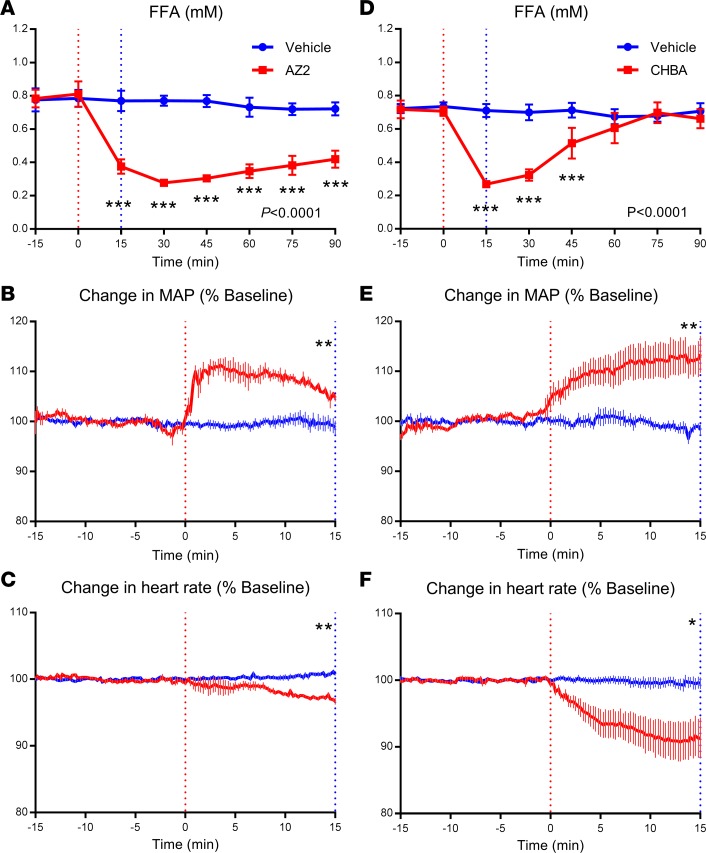
Figure 5. Structurally diverse GPR81 agonists increase blood pressure at doses needed for plasma free fatty acid (FFA) suppression.
Adult male Wistar rats were anesthetized in the fasting state and implanted with jugular and carotid catheters and left to stabilize for 2 hours. Following a 15-minute baseline period (t = –15 to 0 minutes), AZ2 or 3-chloro-5-hydroxybenzoic acid (CHBA) were infused i.v. at 0.9 μmol/kg/min or 10 μmol/kg/min, respectively, for 15 minutes starting at t = 0. Panels to the left show results for AZ2. Right panels show CHBA results. (A and D) Plasma FFA (mM), (B and E) mean arterial pressure (MAP) (percentage baseline period mean), and (C and F) heart rate (HR) (percentage baseline period mean). Results are the mean ± SEM. (A) P is treatment × time interaction (repeated-measures ANOVA). ***P < 0.001 AZ2 versus vehicle (Veh) at the corresponding time period (Bonferroni corrected, Veh n = 4, AZ2 n = 3). (B) **P < 0.01 AZ2 versus Veh average MAP (0–15 minutes) (Student’s t test, Veh n = 4, AZ2 n = 3). (C) **P < 0.01 AZ2 versus Veh average HR (0–15 minutes) (Student’s t test, Veh n = 4, AZ2 n = 3). (D) P is treatment × time interaction (repeated-measures ANOVA). ***P < 0.001 CHBA versus Veh at the corresponding time period (Bonferroni corrected, Veh n = 5, CHBA n = 3). (E) **P < 0.01 AZ2 versus Veh average MAP (0–15 minutes) (Student’s t test, Veh n = 5, CHBA n = 3). (F) *P < 0.01 AZ2 versus Veh average HR (0–15 minutes) (Student’s t test, Veh n = 5, CHBA n = 3).