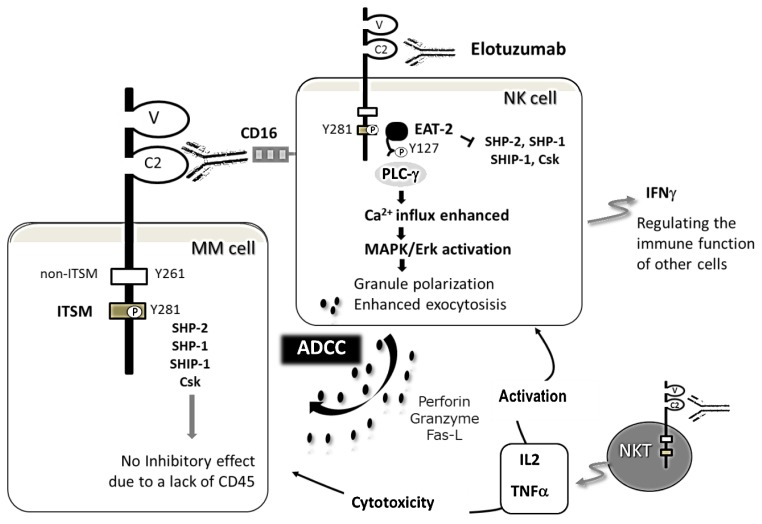
Figure 3. Effect of elotuzumab to NK, NKT, and MM cells.
The primary mechanism of action of elotuzumab is NK cell-mediated ADCC against MM cells. Elotuzumab also directly activates NK and NKT cells, but not MM cells, by its engagement with SLAMF7. This effect results in phosphorylation of tyrosine 281 (Y281) located in ITSMs, thereby recruiting a SLAM-associated adaptor EAT-2. EAT-2 binds to the SH2 domains of PLC-g, and leads to enhanced Ca2+ influx and MAPK/Erk pathway activation, finally resulting in granule polarization and enhanced exocytosis in NK cells. Tyrosine 261 (Y261), needed for the inhibitory function of mouse SLAMF7, is conserved in human SLAMF7.31 NKT cells are also activated via elotuzumab binding, resulting in the accelerated secretion of IL2 and TNFa, which induces the cytotoxicity of NK cells against MM cells.64 Elotuzumab binds to the proximal IgC2 domain of SLAMF 7.