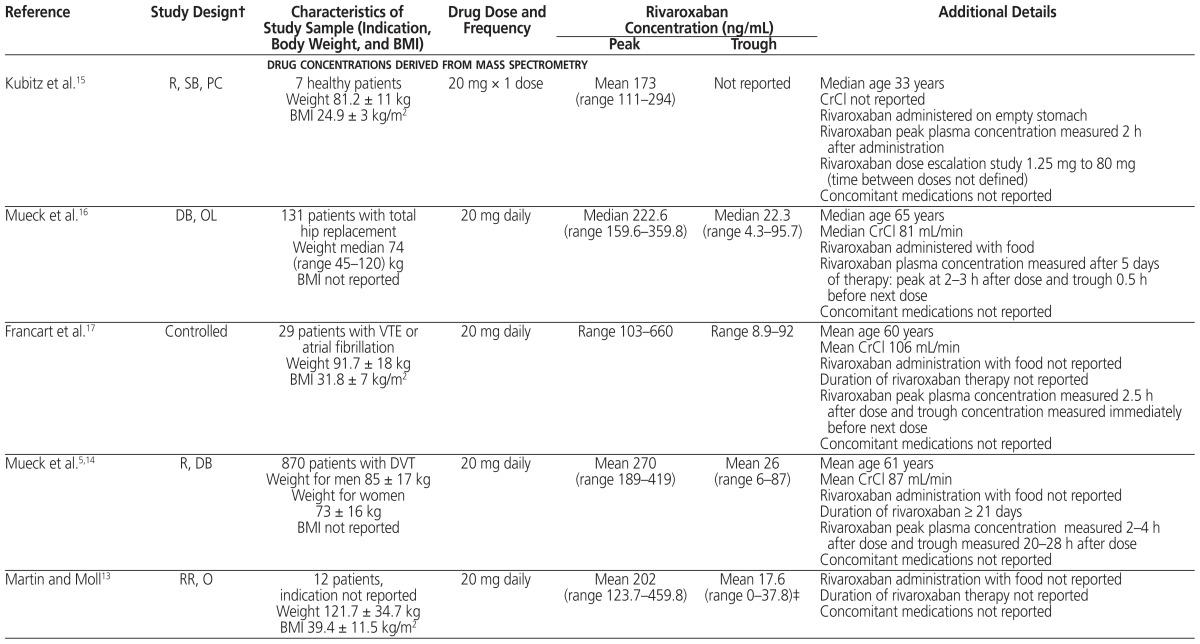
Table 1.
Study Design, Patient Population, and Plasma Rivaroxaban Concentrations Derived from Mass Spectrometry and Anti–Factor Xa Determination*
| Reference | Study Design† | Characteristics of Study Sample (Indication, Body Weight, and BMI) | Drug Dose and Frequency | Rivaroxaban Concentration (ng/mL) | Additional Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| Peak | Trough | |||||
| drug concentrations derived from mass spectrometry | ||||||
| Kubitz et al.15 | R, SB, PC | 7 healthy patients Weight 81.2 ± 11 kg BMI 24.9 ± 3 kg/m2 |
20 mg × 1 dose | Mean 173 (range 111–294) | Not reported | Median age 33 years CrCl not reported Rivaroxaban administered on empty stomach Rivaroxaban peak plasma concentration measured 2 h after administration Rivaroxaban dose escalation study 1.25 mg to 80 mg (time between doses not defined) Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| Mueck et al.16 | DB, OL | 131 patients with total hip replacement Weight median 74 (range 45–120) kg BMI not reported |
20 mg daily | Median 222.6 (range 159.6–359.8) | Median 22.3 (range 4.3–95.7) | Median age 65 years Median CrCl 81 mL/min Rivaroxaban administered with food Rivaroxaban plasma concentration measured after 5 days of therapy: peak at 2–3 h after dose and trough 0.5 h before next dose Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| Francart et al.17 | Controlled | 29 patients with VTE or atrial fibrillation Weight 91.7 ± 18 kg BMI 31.8 ± 7 kg/m2 |
20 mg daily | Range 103–660 | Range 8.9–92 | Mean age 60 years Mean CrCl 106 mL/min Rivaroxaban administration with food not reported Duration of rivaroxaban therapy not reported Rivaroxaban peak plasma concentration measured 2.5 h after dose and trough concentration measured immediately before next dose Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| Mueck et al.5,14 | R, DB | 870 patients with DVT Weight for men 85 ± 17 kg Weight for women 73 ± 16 kg BMI not reported |
20 mg daily | Mean 270 (range 189–419) | Mean 26 (range 6–87) | Mean age 61 years Mean CrCl 87 mL/min Rivaroxaban administration with food not reported Duration of rivaroxaban ≥ 21 days Rivaroxaban peak plasma concentration measured 2–4 h after dose and trough measured 20–28 h after dose Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| Martin and Moll13 | RR, O | 12 patients, indication not reported Weight 121.7 ± 34.7 kg BMI 39.4 ± 11.5 kg/m2 |
20 mg daily | Mean 202 (range 123.7–459.8) | Mean 17.6 (range 0–37.8)‡ | Rivaroxaban administration with food not reported Duration of rivaroxaban therapy not reported Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| drug concentrations derived from anti-Xa | ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Lang et al.10 | OL | Sample size and indication not reported (373 blood samples analyzed) Weight and BMI not reported |
15 mg daily | 196.6 ± 117 | 93.8 ± 70 | No documentation of patient demographics CrCl not reported Rivaroxaban administration with food not reported Duration of rivaroxaban therapy not reported Rivaroxaban anti-Xa measured at < 3 h, 3–12 h, 12–19 h, and > 19 h after dose Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| 20 mg daily | 213.8 ± 138 | 64.2 ± 64 | ||||
|
| ||||||
| Ikeda and Tachibana11 | P | 36 patients with atrial fibrillation Weight 60.3 ± 11.7 kg BMI 23.6 ± 2.5 kg/m2 |
10 mg or 15 mg daily | Mean 467.3 (range 99–821.3) | Mean 62.5 (range 0–290.3) | Mean age 74 years Mean CrCl 69 mL/min Mean CHADS2 score 2.1 Rivaroxaban administration with food not reported Rivaroxaban anti-Xa measured after 7–911 days: peak 2–5 h after dose and trough 20–26 h after dose Concomitant medication classes reported |
|
| ||||||
| Testa et al.12 | P, O | 71 patients with atrial fibrillation (at 3 clinics) Weight 74 ± 16.5 kg BMI 25.4 ± 5.6 kg/m2 |
15 mg daily | Clinic A: mean 190 (range 77–355) Clinic B: mean 229 (range 149–365) Clinic C: mean 205 (range 85–39) |
Clinic A: mean 25 (range 17–49) Clinic B: mean 26 (range 19–34) Clinic C: mean 32 (range 0–88) |
Mean age 74 years CrCl not reported Mean CHADS2 score 2.4 Rivaroxaban administered with food Rivaroxaban anti-Xa measured after 15–25 days: peak 2 h after dose and trough 24 h after dose Concomitant medications not reported |
|
| ||||||
| 20 mg daily | Clinic A: mean 247 (range 61–449) Clinic B: mean 229 (range 65–370) Clinic C: mean 231 (range 138–341) |
Clinic A: mean 39 (range 16–74) Clinic B: mean 41 (range 16–106) Clinic C: mean 43 (range 5–119) |
||||
|
| ||||||
| Jayakody Arachchillage et al.18 | OL | 167 patients with VTE Weight < 50 kg, 50–120 kg, or> 120 kg§ BMI not reported |
20 mg daily | Weight < 50 kg: median 460 (95% CI 380–601) Weight 50–120 kg: median 308 (95% CI 308–381) Weight > 120 kg: median 281 (95% CI 242–327)¶ |
Not reported | Mean age 59 years CrCl > 30 mL/min Rivaroxaban administration with food not reported Duration of rivaroxaban therapy not reported Rivaroxaban peak anti-Xa measured 2–4 h after dose Concomitant medications not reported |
AF = atrial fibrillation, CI = confidence interval, CrCl = creatinine clearance, DVT = deep vein thrombosis, NR = not reported, VTE = venous thromboembolism.
All data are reported as mean ± standard deviation, except where indicated otherwise.
Abbreviations used for aspects of study design: DB = double-blind, O = observational, OL = open label, P = prospective, PC = placebo-controlled, R = randomized, RR = retrospective review, SB = single-blind.
Five of the 12 patients had trough rivaroxaban determined by anti-Xa.
For 18 patients, weight < 50 kg (mean 43 kg, range 38–49 kg); for 105 patients, weight 50–120 kg (mean 86 kg, range 50–120 kg); for 44 patients, weight > 120 kg (mean 135 kg, range 121–186 kg).
Patients weighing < 50 kg had significantly higher rivaroxaban concentrations than patients weighing 50–120 kg or > 120 kg (p = 0.005).