Fig. 6.
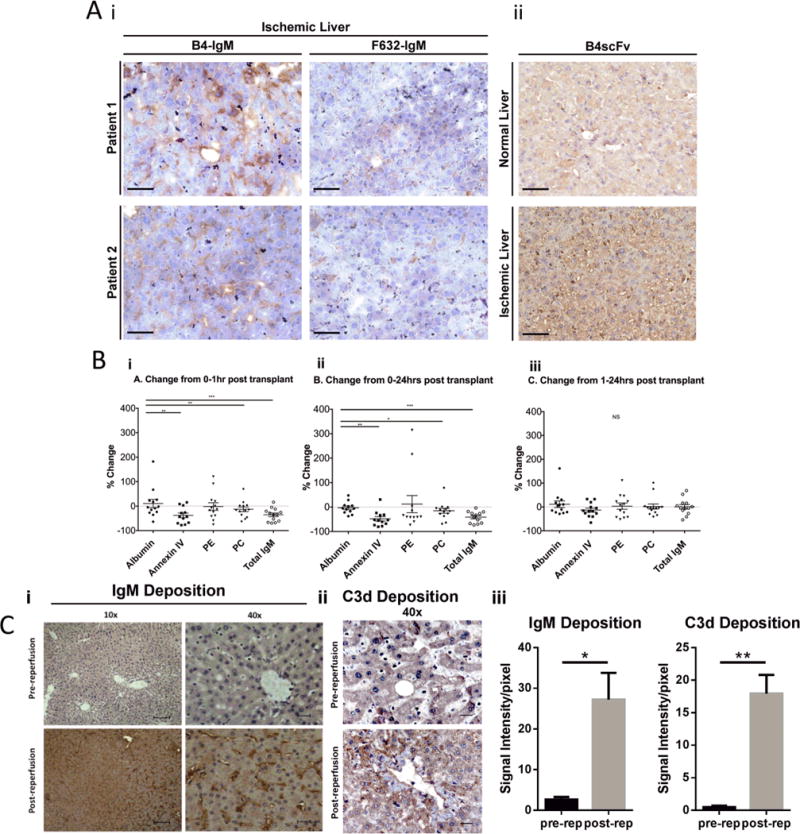
Analysis of clinical samples. (A) B4 antigen is expressed in ischemic but not normal human liver samples. “Ischemic” liver biopsies were obtained from ischemic human donor livers prior to transplantation, and “normal” liver samples were taken from areas of normal pathology following resection of hepatic hemangioma. (A) Shows immunohistochemical staining of sections using (A.i) B4 mAb, control F632 mAb, and (A.ii) B4scFv as indicated. Representative images from 3 samples from 3 patients. Scale bar represents 50 uM. (B) Serum levels of specific pathogenic natural IgM antibodies decrease following human liver transplantation. Serum levels of IgM antibodies against annexin IV, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylcholine (PC), and total IgM and albumin were measured by ELISA in serial serum samples taken from patients undergoing liver transplantation. Serum was harvested at three time points: just prior to transplantation (baseline= 0 hour), 1 hour, and 24 hours after transplantation. (B.i.) Percent change from 0–1 hour post transplantation. (B.ii) Percent change from 0–24 hours post transplantation. (B.iii) Percent change from 1–24 hours post transplantation. Each data point represents one patient, n = 13. Data representative of 3 separate experiments. *** p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. (C) Immunofluorescence staining for IgM and C3d in human livers pre-transplantation and 1 hour post reperfusion. (Ci,ii) Representative images, n = 3 patients. Scale bar = 50 uM (40×). (Ciii) Quantification of fluorescence intensity of IgM and C3d staining. Mean+/− SEM, n = 3, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.
