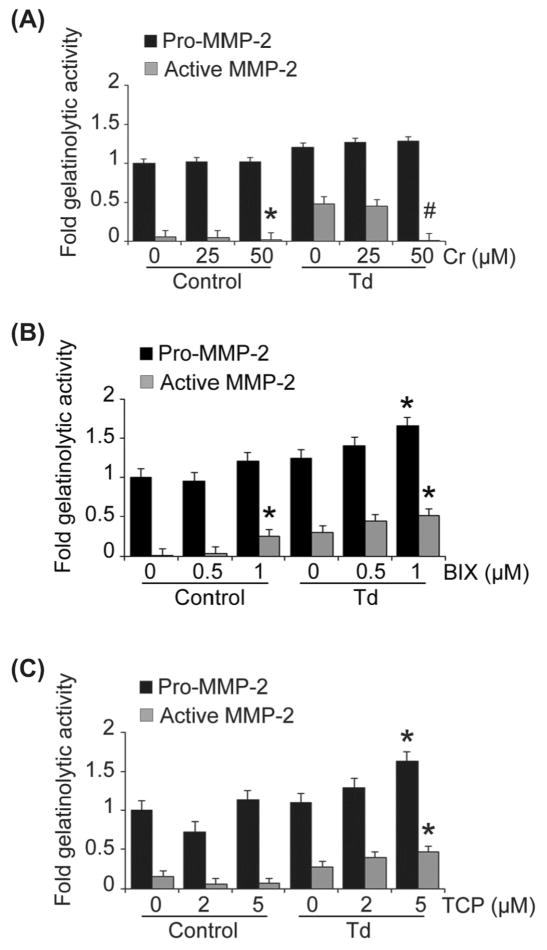
Figure 7. Inhibition of different chromatin modification enzymes mediate alterations in levels of expression and activation of MMP-2 in Td-challenged and control PDL cell cultures.
PDL cells were pre-treated with enzyme inhibitors at the indicated concentrations as follows: curcumin (histone acetyltransferase inhibitor) for two hours (A), 0.5 μM and 1 μM BIX-01294 (histone methyltransferase inhibitor) for two days (B), and 2 μM and 5 μM tranylcypromine/TCP (histone demethylase inhibitor) for four days (C). The cells were then challenged with T. denticola (Td) at MOI = 100 or media control for two hours, then incubated for three days. The conditioned medium and cell lysates were collected for zymography. Shown are densitometric analyses of pro-MMP-2 (72kDa) and active MMP-2 (64kDa) detected by gelatin zymography. The X-axis represents different concentrations of enzyme inhibitors in the control and Td groups. The Y-axis represents fold-gelatinolytic activity of the pro-MMP-2 and active MMP-2 relative to unchallenged and untreated controls. Panels: A, curcurmin (Cr); B, BIX-01294 (BIX); C, tranylcypromine (TCP). The experiments were repeated three times in triplicate. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. (*) represents p ≤ 0.05 compared to the “0” concentration in the same group. (#) represents p ≤ 0.001 compared to the “0” concentration in the same group.