Figure 2. Deficiency of TNFR1 receptors prevents JNK activation in olfactory sensory neurons.
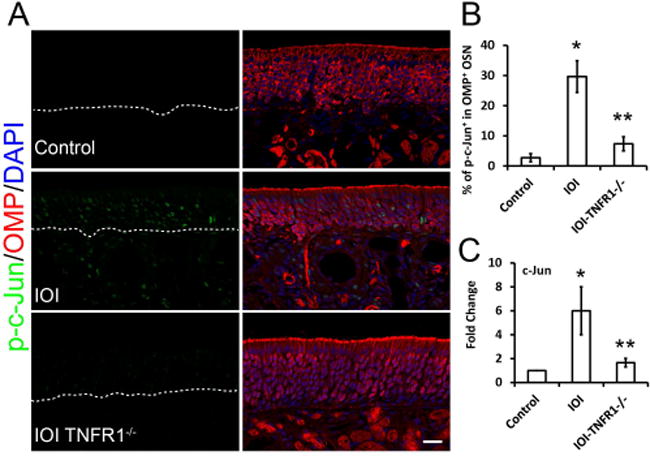
(A) Co-staining of phosphorylated c-Jun (p-c-Jun) with OMP in olfactory epithelium. Positive nuclei staining of p-c-Jun in an IOI (inducible olfactory inflammation) mouse model indicated JNK signaling activation. In IOI background, the knockout of the TNF-α receptor 1 (TNFR1) blocked JNK activation, suggesting the key role of TNFR1 in JNK activation in the TNF-α pathway.(B) Ratio of p-c-Jun+/ OMP+ population in OMP+ OSNs. *P = 0.0012, **P = 0.005.(C) Q-PCR analysis of JNK target gene c-Jun mRNA expression. IOI mice were treated with Dox for 3 weeks (n = 3), olfactory mucosa was collected for real-time PCR analysis. *P = 0.0002. **P = 0.011. Scale bar, 20 μm.
