Fig. 1.
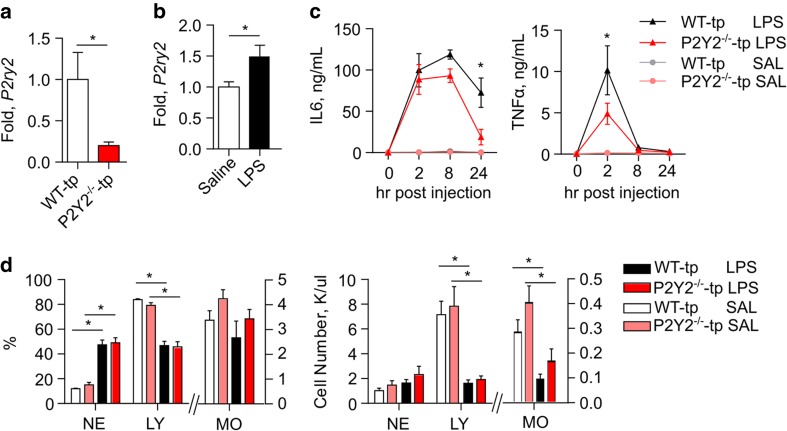
P2Y2−/−-tp mice challenged acutely with LPS are protected from inflammation. P2y2r mRNA levels in blood of WT-tp and P2Y2−/−-tp mice were measured by qRT-PCR and revealed a significant decrease in the mice transplanted with P2Y2 null marrow (N = 12, mean ± SEM, p < 0.006 by Mann-Whitney test) (a). WT-tp and P2Y2−/−-tp mice were dosed i.p. with either saline or 2 mg/kg LPS for 24 h (b–d). Expression of P2y2r mRNA was measured in blood from WT-tp mice and normalized to B2M revealing a significant increase in P2y2r mRNA upon LPS treatment (N = 5, mean ± SEM, p < 0.05 by Student’s t test) (b). Serum IL6 and TNFα levels were measured by ELISA over the 24-h period. P2Y2−/−-tp mice have significantly lower serum IL6 at 24 h and significantly lower TNFα at 2 h (N = 6, mean ± SEM, p < 0.0001 by two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test) (c). Hemavet analysis of immune cells from blood reveals no difference in immune cell distribution or absolute number between WT and P2Y2−/−-tp mice after 24 h of LPS treatment (N = 6, mean ± SEM), *p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (d)