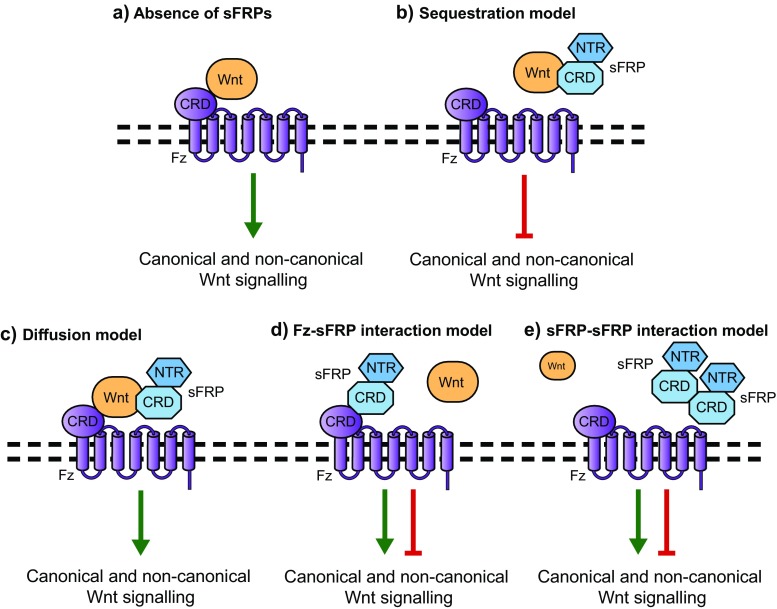
Fig. 2.
Possible mechanisms by which sFRPs could modulate Wnt signalling. (a) In the absence of sFRPs, Wnt ligands are free to interact with Fz receptors and activate downstream Wnt signaling. (b) sFRPs can sequester Wnt ligands through the CRD or NTR domain, thereby acting as a classical Wnt antagonist. (c) sFRPs may bind Wnt ligands, and aid in their stability and diffusion in the extracellular space. (d) sFRPs may bind Fz receptors, and form signalling active or inactive complexes. (e) sFRPs interact with each other in the extracellular space and modulate one another’s activity