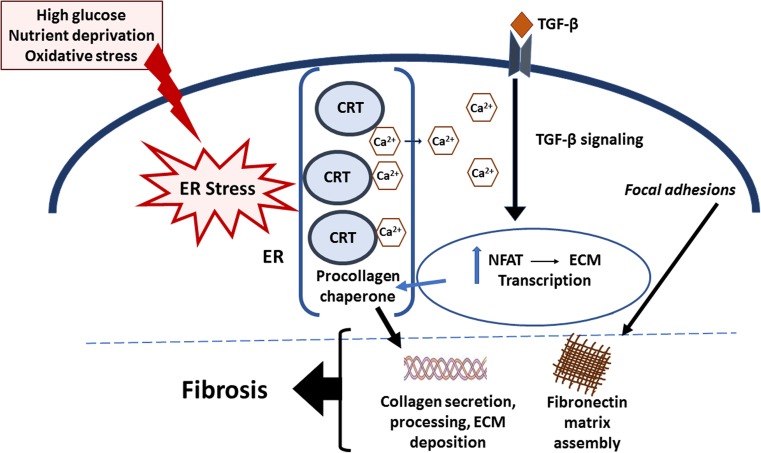
Fig. 1.
Model of CRT regulation of TGF-β-stimulated ECM production in fibrosis. Factors such as high glucose, nutrient deprivation, and oxidative stress trigger ER stress. ER stress increases CRT levels. In turn, CRT mediates Ca2+ release from the ER, resulting in an increase in cytosolic Ca2+, which stimulates increased calcineurin activity and NFAT dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Importantly, TGF-β stimulates increased cytosolic Ca2+ in a CRT-dependent manner: CRT is required for TGF-β stimulation of fibronectin and collagen I transcription through NFAT. In addition, ER CRT stimulates cell adhesion and fibronectin matrix assembly, and acts as a collagen chaperone assisting in collagen secretion and procollagen processing into the ECM. Furthermore, CRT is important for TGF-β stimulated EMT. These actions of CRT are thought to underlie its role in fibrogenesis