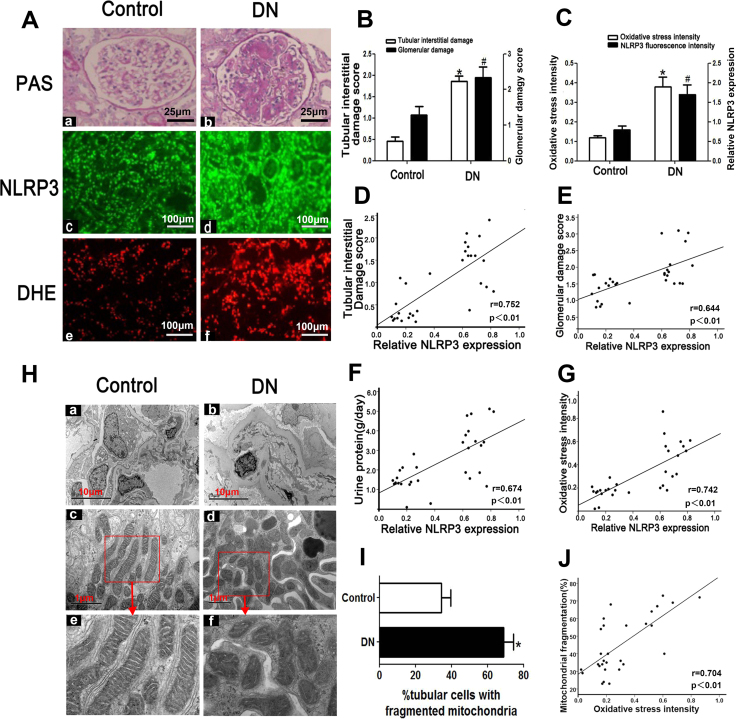
Fig. 1.
Tubular injury, NLRP3 expression and ROS production are enhanced in the kidney tissues of patients with DN.A: PAS and DHE staining showing that tubular injury, interstitial fibrosis (top panels) and ROS production (bottom panels) are enhanced in the kidney tissues of patients with DN. IF revealed that NLRP3 expression is increased in patients with DN (middle panels) (magnification × 400). B: Tubulo-interstitial damage and glomerular damage scores. C: Quantification of DHE signal intensity and NLRP3 expression. D-G: Analysis of the correlations between NLRP3 expression and tubulo-interstitial damage (D), glomerular damage (E), urine protein (F) and oxidative stress (G) in the kidneys of patients with DN. H: Representative image of the electron microscopy analysis. The number of tubular cells with mitochondrial fragmentation was notably increased in the renal tissues of patients with DN (Hd, f) compared with those of control patients (Hc, e) (magnification × 10,000).I: Relative percentage of renal tubular cells with fragmented mitochondria. J: Correlation between mitochondrial fragmentation in tubular cells and oxidative stress. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.05 versus control. Values are the mean ± SE. n = 15.