Figure 7.
Comparison with Other Paused Complexes and Model for the his-Pause
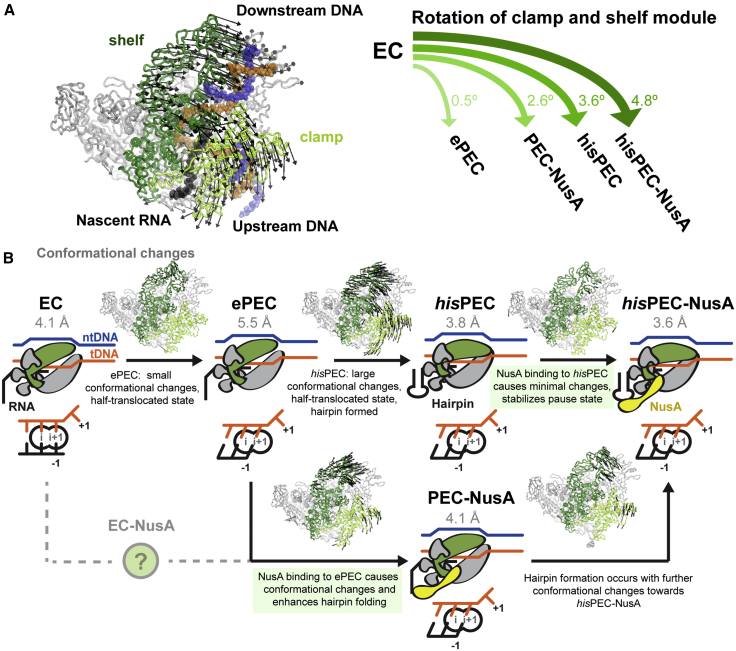
(A) The shelf and clamp module rotate relative to their position in a EC (left). The extent of rotation is different for various intermediates determined in this work (PEC-NusA, hisPEC-NusA) and by Kang et al. (2018) (ePEC, hisPEC).
(B) Model for RNAP entering the hairpin and NusA stabilized state at the his-pause. RNAP may convert to an ePEC when it encounters a pause sequence with a half-translocated RNA-DNA hybrid. Conformational changes in clamp and shelf module can be trapped by hairpin formation. Binding of NusA induces minimal additional changes and stabilizes paused conformation (top). Alternatively, NusA can bind an EC (resulting RNAP conformation unknown) or ePEC with half-translocated hybrid. RNAP adopts an intermediate conformation as a result of NusA binding. Hairpin formation (stimulated by NusA) leads to the final paused RNAP conformation (bottom). Active site schematics are shown (note that a pre-translocated EC was modeled based on 6ALH).
See also Table S1.