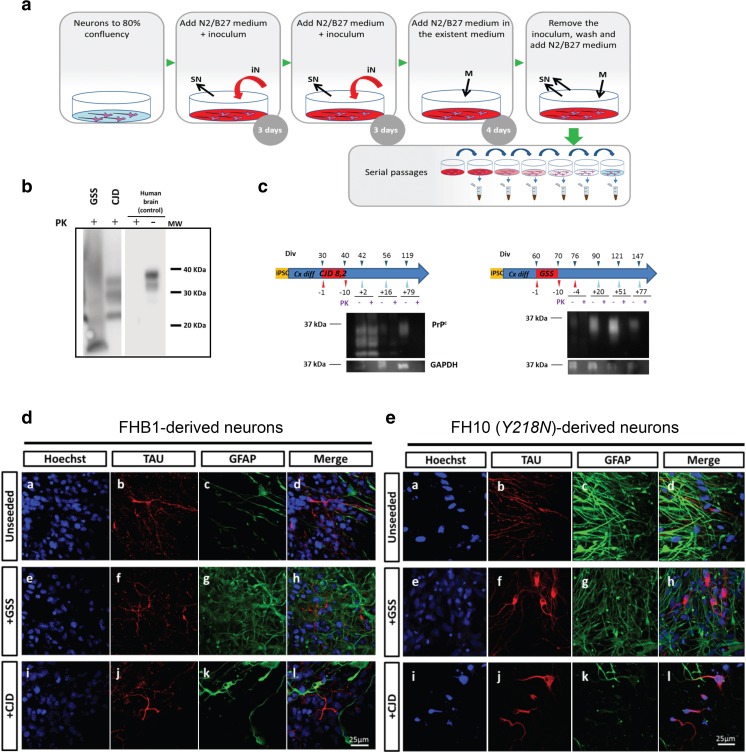
Fig. 6.
Infectivity assay with brain inoculates. (a) Schematic representation of the inoculation protocol: infective brain homogenates were added at day 0 and day 3 and removed at day 10; cells were subsequently passaged several times to remove the inocula. (b) Inocula from the sources (10% of brain homogenates, see Methods for details) were processed to show PK-resistant PrP signal. GSS: human brain diagnosed of Y218N. CJD: human brain diagnosed of a sporadic CJD MM1. CJD samples were digested with 10–50 μg/ml of proteinase K (PK) and subjected to a standard biochemical analysis. GSS sample was treated as an atypical prion sample (see Methods). The samples were analyzed using the monoclonal antibody 3F4. MW: Molecular marker. (c) Representative examples of Western blot detection of PK-resistant PrP forms following inoculation with CJD and GSS brain samples. Note that PK-resistant PrP was only detected (when present) for the first 2 weeks after the infection. (d) Morphological analyses 2 months later revealed little effect of these inoculates in control neurons while mutant Y218N cultures (e) showed fewer neurons with marked cytoplasmic redistribution of Tau signal (b, f, j) and enhanced immunoreactivity for GFAP. Scale bars: 25 μm