Fig. 1.
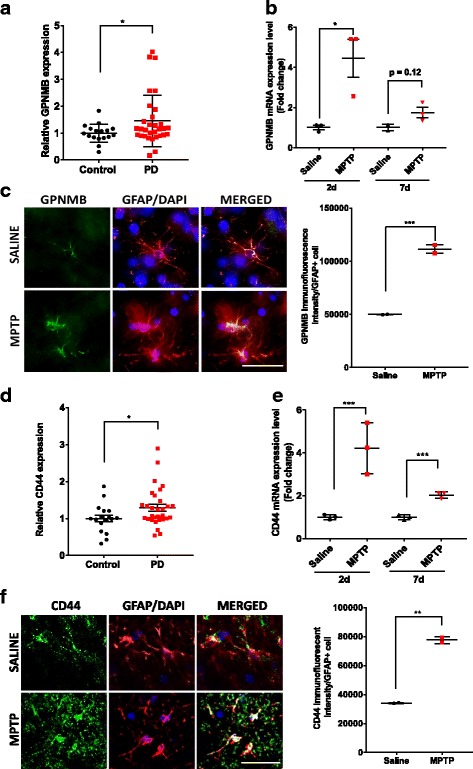
Increased GPNMB and CD44 levels in PD patients and an acute MPTP mouse model. a Gene expression of GPNMB is increased in the substantia nigra of PD patients (n = 22 males and n = 9 females) compared to age-matched controls (n = 10 males and n = 7 females). GEO numbers were normalized to 1 to generate relative expression values and allow comparison between datasets. b GPNMB gene expression in the mouse striatum by qPCR following an acute injection of MPTP in mice and sacrificed at 2 and 7 days post injection. c Representative images of immunofluorescent confocal microscopy of GPNMB (green), GFAP (red), and DAPI nuclear stain (blue) at × 40 magnification following an acute injection of saline or MPTP, scale bar and 50 μm. d Gene expression of CD44 in human PD patients examined by microarray on the GEO demonstrating a significant increase in CD44 gene expression in the SN of PD patients. e–f CD44 gene expression and protein levels in the mouse striatum by e qPCR and immunofluorescent confocal microscopy of CD44 (green), GFAP (red), and DAPI nuclear stain (blue) at f × 40 magnification following an acute injection of Saline or MPTP, scale bar and 50 μm. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences between PD and age-matched controls or MPTP and saline controls (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001)
