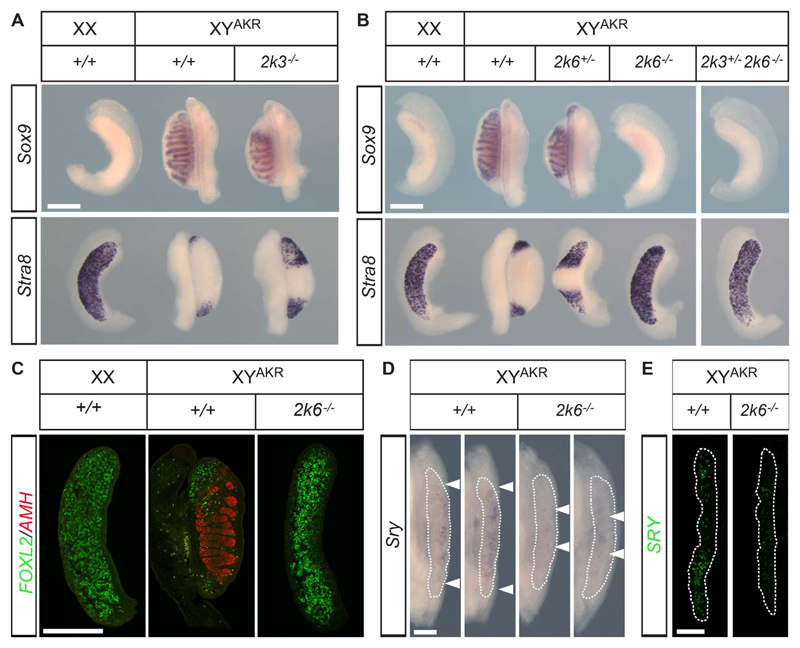
Fig. 3. Gonadal sex reversal phenotype at 14.5 dpc in MAP2K6-deficient embryos on the B6.YAKR background.
A) WMISH with Sox9 and Stra8 probes showing loss of Sox9 signal, abnormal cord morphology, and extensive expression of Stra8 in Map2k3 null mutant gonads compared to wild-type controls. Control XY gonads (center, lower panel) exhibit small Stra8-positive regions due to transient ovotestis formation associated with the reduced functionality of the SryAKR allele on B6. Bar = 500 μm. B) WMISH with Sox9 and Stra8 probes reveals complete gonadal sex reversal in Map2k6-deficient gonads and compound mutant gonads (Map2k3+/−, Map2k6−/−), associated with overt ovarian morphology, loss of Sox9, and ectopic Stra8 expression throughout. Heterozygous mutant gonads (Map2k6+/−) may also exhibit large Stra8-positive regions and reduced Sox9 expression at the poles and abnormal cord morphology, in contrast to wild-type controls. Bar = 500 μm. C) Immunostaining of gonadal tissue sections comparing MAP2K6-deficient embryos and wild-type controls. AMH (red) is detected in testis cords of control gonads but is absent from mutant gonads. The ovarian granulosa cell marker FOXL2 (green) is detected throughout the XY mutant gonad, as it is in XX controls. Some polar FOXL2 is detected in the B6.YAKR wild-type control for reasons explained above. Bar = 500 μm. D) WMISH at 11.25 dpc with an Sry probe shows clear expression throughout the gonad (area within white dotted lines; limits of expression indicated by arrowheads) in two B6.YAKR wild-type (+/+) controls; but signal is negligible and restricted to central regions (indicated by arrowheads) in two MAP2K6-deficient gonads (2k6−/−) on the same background at exactly the same stage (16 ts). Bar = 200 μm. E) Immunostaining with an anti-SRY antibody at 17 ts reveals a large number of SRY-positive cells in the control (+/+) gonad (area within white dotted line), but few SRY-positive cells in a stage-matched mutant (2k6−/−) gonad. Bar = 200 μm.