Figure 1.
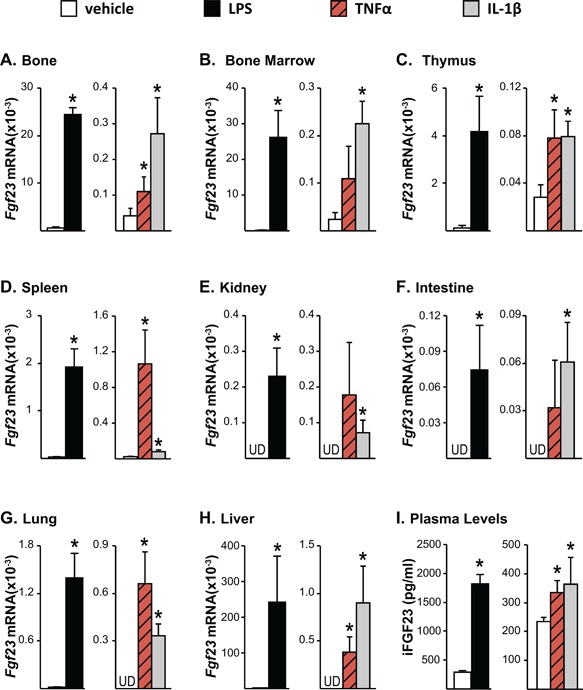
Inflammation increases Fgf23 mRNA expression in bone and non‐osseous tissues. Twelve‐month‐old female mice were injected intraperitoneally (ip) with 10 mg/kg of LPS or PBS. Eight‐week‐old female mice were injected with 2 μg of recombinant TNFα, 50 ng/g of IL‐1β, or PBS. The tissues and blood were collected 3 hours after TNFα and 6 hours after LPS or IL‐1β injection. (A–H) Fgf23 mRNA levels were measured by quantitative RT‐PCR and normalized to beta‐actin mRNA levels. (I) Blood was collected by cardiac puncture, and circulating intact FGF23 (iFGF23) levels were measured in EDTA plasma. (A–I) All values represent mean ± SD of 3 to 4 mice/group. All statistical comparisons were performed using Student's t test. *p < 0.05 compared with vehicle controls. UD indicates that Fgf23 levels were undetectable by RT‐PCR.
